Detailed explanation of rice planting technology (with rice pest control technology)
Rice is a common and important variety in agricultural planting in China. Today, Xiaobian will talk about rice planting technology and rice pest control technology. Rice novice friends should learn more.

1. Rice planting technology
1.1 Site selection
When selecting the location of the paddy field, it should be ensured that the soil texture is good, the irrigation water source is close to the same time and there is no pollution. The rice, whether it is light, temperature or water source, can meet the requirements of relevant standards.
1.2 Selection
As the main food crops in China, rice has a wide variety. Before planting, it needs to be selected in combination with local climate and soil conditions. In the process of rice selection, one should choose varieties with stable yield, high yield, disease resistance and lodging resistance to ensure seed purity and reduce the rate of hybrid plants. Second, it should be combined with machine selection, wind power, salt water selection and other methods to remove the existing Shibuya, leaving seeds full of particles. After the selection is completed, the mixed carbendazim solution should be used to soak the seeds to improve the resistance of rice to pests and diseases.
1.3 Sowing
Artificial sowing or mechanical sowing, such as artificial sowing, per acre of seeding should be selected according to the topography of the rice paddy and the scale of rice planting. 1. The early rice is planted in a batch of 10~15 kilograms, and the sowing amount of hybrid rice is about 6 kilograms. 2. The amount of hybrid rice in the middle rice should be controlled at 3 kg. 3, the amount of hybrid rice in the late rice hybrid is about 3 kilograms (such as the use of early hybrids to control the amount of autumn in the 5 to 8 kilograms is appropriate).
1.4 nursery
The seedlings can be carried out in a special nursery center or in the field. In the nursery stage, it is necessary to ensure that the flat soil in the field is moderately permeable and to ensure the growth of the seedlings. When the seedlings reach a certain height, they can continue to transplant.
1.5 Insert
Transplanting is a very important part of rice planting. It must be ensured that the depth of seedlings inserted into the silt is reasonable and orderly. The transplanting method also includes both manual and mechanical methods. In comparison, mechanical transplanting is more efficient, but the rice field topography must be flat. If the undulation is large or the shape is irregular, the quality of the transplanting will be affected. During the transplanting process, heavy rain should be avoided to ensure that the seedlings are moving from north to south, and the seedlings with strong roots can be used to enhance the survival rate.
1.6 Fertilization
After the transplanting, the fertilizer should be applied in time to provide the rice with the nutrients needed for rapid growth to ensure the smooth survival of the rice. In general, early rice should be applied with 35% compound fertilizer, and the applied amount is 600-650kg per hectare. The application rate of late rice should be appropriately increased, and it should be controlled at 650~750kg per hectare. Considering the high-quality and high-yield rice stalks are fine, in the young panicle differentiation or jointing stage, the amount of nitrogen fertilizer applied needs to be strictly controlled.
1.7 Irrigation
Irrigation is one of the most important procedures in rice cultivation. There are several basic principles that should be adhered to. One is shallow water transplanting to ensure uniform and straight seedlings; the second is deep-water living, which requires timely irrigation after transplanting. The amount of water is controlled in the lower part of the ear, to meet the growth requirements of rice seedlings; the third is thin water sputum. When the rice is in the tillering stage, the water quantity needs to be controlled. If necessary, drain and dry to ensure cracks in the field, and white roots can be seen in the gap; The fourth is the long water of the foot. In the rice heading stage, the water supply should be sufficient. The water depth should be about 5~10cm to ensure the growth of the roots of the rice. The fifth is the wet and dry seeds. In simple terms, it is diving in the heading stage. Irrigation, 5~7d before harvesting, can not be watered or too much.
1.8 weeding
When conditions permit, manual weeding should be chosen as much as possible, or ducks should be staked in paddy fields to effectively control weeds and minimize the use of chemicals. If the rice planting area is large, some low-toxic herbicides, such as oxaloin and turpentine, can be selected appropriately, and the concentration and dosage should be controlled to avoid large-scale death of rice.

2. Rice pest control technology
2.1 Blight
The causes of blight are mainly low temperature, large temperature difference or insufficient light, large amount of seeds, etc., which are characterized by the wilt of seedlings and the decay of the base of the stem. In severe cases, the seedlings of rice seedlings may die. For the control of blight, one can apply a pH of 4.5 acid water in one leaf, one heart and two leaves, and if a disease is found, it can be applied with a suitable strong agent or spray 2500 times 30%. Rui Miaoqing.
2.2 Plague
Plasmosis, also known as rice blast, is caused by excessive application of nitrogen fertilizer or improper water control, which will result in large-scale reduction of rice production and early prevention. You can choose the medicine and the scientific cultivation method to prevent rice plague. For example, choose 20% tricyclazole wettable powder to soak the rice seeds, or 75% Fengdeng WP 2000 times to soak the rice seedlings, then After transplanting for 30 minutes, transplanting can effectively prevent rice blast. If rice blast occurs during the jointing and tillering stage of rice, it can be controlled by Fuji No. 1 emulsifiable concentrate or 40% rice glutinous emulsifiable concentrate 1000 times.
2.3 Sheath blight
Sheath blight is one of the most common diseases in rice. It is common in early rice, which leads to an increase in empty shell rate, insufficient grain, and serious plant death. The prevention and control of sheath blight should be based on agricultural measures. On the one hand, water and fertilizer management should be done well, nitrogen and phosphate fertilizers should be applied reasonably, potash and heart palpitations should be appropriately increased to ensure adequate base fertilizer, and the application of nitrogen fertilizer should be minimized in the middle of rice growth; On the other hand, we should pay attention to drug control. For large-scale rice fields, we can spray with Jinggangmycin high-concentration powder or 5% Jinggangmycin water. The timing of spraying should be sunny, or at least 2 hours after spraying. It is raining to ensure the full effect of the drug. If the disease rate exceeds 30%, it is necessary to concentrate on the middle and lower parts of rice.
2.4 Locust pests
Aphids have an effect on rice earing, which in turn leads to a decline in yield. The control of aphid pests is generally based on drug control. It can be controlled by 13.5% drill heart emulsifiable concentrate, 15% thunderstone emulsifiable concentrate or 13.5% duel emulsifiable concentrate per hectare of rice. The dosage is 1.35L, 1.35L and 0.75L.
2.5 Rice planthopper pests
There are many types of rice planthoppers. The more common ones are brown planthopper, gray planthopper, and white-backed planthopper. The pests will hide in the leaf sheath and stem tissue of the lower part of the rice plant, causing the stem tissue to be destroyed, and the rice plant will gradually wither or even die. For the prevention and control of the fly worm, it is necessary to accurately grasp the peak of the small nymph, and realize the cofferdam of the small nymph by one-time application of the drug, and spray it with 40% of the 40% dimethoate emulsion and 800-1000 kg of water.

All in all, as the main food crop in China, rice is cultivated in many areas. From the perspective of ensuring stable and high yield of rice, agricultural technicians need to start from the regional climate conditions, do research on rice planting techniques, and emphasize the prevention and control of common pests and diseases. Ensure the healthy growth of rice.
The above is the rice planting technology and rice pest control technology compiled by Huinong. I have learned it? If you want to know more about agricultural technology, please pay attention to the Hui Nong School!
New product of U85 micro laser distance sensors use highly focused class 2 laser to detect objects or measure distances, and can return a measured value via varieties intface( serial, usb, rs232, rs485, bluetooth etc.). The electronic distance sensor is a very small Laser Distance Sensor, but high resolution up to 1mm and long distance measuring sensor - teachable measuring range of up to 30m. Extremely accurate distance sensing sensors, errors down to ± 1mm. And the mini sensors and measurements support continuous measurement function, great for compact solutions(eg: robots) with the smallest Laser Distance Sensor of the world!
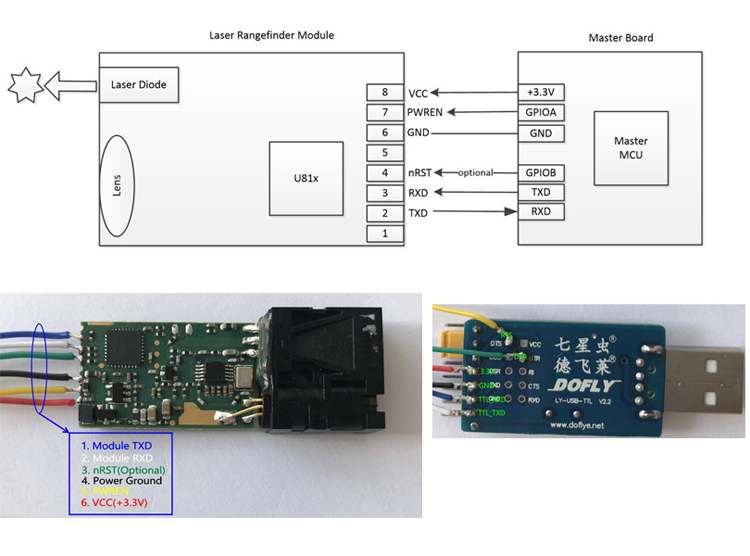
Parameters of U85:
Accuracy
±1 mm (0.04 inch)
Measuring Unit
mm
Measuring Range (without Reflection)
0.03-20m/0.03-30m
Measuring Time
0.1~3 seconds
Laser Class
Class II
Laser Type
620nm-690nm, <1mW
Size
41*17*7mm (±1 mm)
Weight
About 4g
Voltage
DC2.0~3V
Electrical Level
TTL/CMOS
Certifications
CTNT, FDA, CE, FCC, RoHS, etc.
Operating Temperature
0-40 ℃ (32-104 ℉ )
Storage Temperature
-25~60 ℃ (-13~140 ℉)
Mini Laser Distance Sensor,Optical Laser Distance Sensor,Smallest Laser Range Sonsor,Laser Measuring Sensor
Chengdu JRT Meter Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.infrareddistancesensor.com