Fruit tree fertilizer and application technology
2024-09-14 03:02:47
1. The correct use of farmyard fertilizers and fertilizers is one of the key links in the production of pollution-free fruit, which should arouse enough attention from us. The national agricultural industry standards promulgated and implemented recently by the Ministry of Agriculture have clearly stipulated the guidelines for the use of fertilizers for the production of green foods (fruits), requiring that the principles of fertilization be organic fertilizers, supplemented by chemical fertilizers, and maintain or increase soil fertility and soil. The microbial activity and the fertilizer used at the same time should not adversely affect the orchard environment and fruit quality. We combine the implementation of standards and the demand for fertilizers for fruit production to illustrate the fruit tree fertilizers and their use. I. Types of Fertilizers (1) Fertilizer Types Allowed The farm fertilizer refers to various organic fertilizers that are locally sourced and used on site. It consists of a large number of biological substances, animal and plant residues, excreta, and biological waste. It is rich in organic matter and various macro and trace elements required for humus and fruit trees. It also contains hormones, vitamins, and antibiotics. . It is characterized by a wide range of sources, great potential, complete nutrients, a long and stable fertilizer effect, and a slow-lasting fertilizer; farmer fertilization can improve soil and improve soil fertility, and is the main fertilizer for orchards. It mainly includes compost, manure, manure, biogas fertilizer, green manure, crop straw fertilizer, mud fertilizer and cake fertilizer. (1) Compost: Compost is the use of crop straws, weeds, leaves, garbage and other organic wastes as the main raw materials, and a certain amount of excrement, sewage and a small amount of mud to compile a class of organisms formed by aerobic microorganisms. fertilizer. The process of composting is the process by which microorganisms decompose organic matter, so it is necessary to create conditions suitable for microbial activity. Composting is carried out in high temperature seasons. The heap should maintain sufficient moisture. It is advisable to control the moisture to 65% to 75% of wet weight. In order to facilitate microbial activity, attention should also be paid to the ventilation of the heap. After maturity, it is used as base fertilizer. (2) Manure fertilizer: The materials used are basically the same as compost, except that under the flooding conditions, the microorganisms are fermented by anaerobic fermentation to form a kind of organic fertilizer. (3) Manure: Also known as circulatory manure, it is a manure that is produced by using urine and feces in the livestock circle, weeds, deciduous soil, and peat soil. Ring fertilizer contains three elements: nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. The potassium content is high and can be directly absorbed and utilized by fruit trees. (4) Biogas fertilizer: In the closed biogas digester, organic matter is produced by bio-fermentation under the conditions of outgassing to produce by-products of biogas, consisting mainly of biogas fertilizer and biogas slag. (5) Crop Straw Manure: Fertilizer directly returned to the field with wheat straw, rice straw, corn stalks, soybean stalks, and rape straw. (6) Mud fertilizer: Fertilizers made from uncontaminated river mud, pond mud, gully mud, harbor mud, lake mud, etc. that are decomposed by anaerobic microorganisms. (7) Cake Fertilizer: Fertilizers made from various oil-containing seeds that have been pressed and deoiled, such as rapeseed cakes, cottonseed cakes, bean cakes, peanut cakes, and sesame cakes. (8) Green manure: Green manure is also one of the sources of base fertilizer in orchards. It has high fertilizer efficiency. There are two main ways to use green manure: From the bud of green manure to the early flowering stage, it is crushed to about 10 cm. Spread it evenly over the fields and let it dry in the soil for a long time. In general, 1000 kg to 1500 kg per acre is appropriate. An orchard with irrigated conditions can be used to inject water once a day or two in a day, which is conducive to green manure; water-free pouring can wait until the rainy season comes. 2 Concentrated into the tree. That is, dig a trench 60 cm deep, 60 cm wide, and 150 cm long along the outer edge of the canopy. Cut the green manure and dry it. Crush it into 10 cm or so, 50 kg to 70 kg per pit, mix the green manure with the soil. Fill in the pit, fill with the practical, fill enough water after application. About 20 days after fertilization, new roots can begin to appear in the pit. The commonly used green manure plants in orchards include Amorpha fruticosa, Ranunculus trifoliata, Clover, Rhinoceros, Sesbania, Sanda, Mung bean and so on. (9) Human and animal urine: It is a mixture of human and animal feces and urine, rich in organic matter and various nutrients. The human fecal nitrogen content is relatively high and the livestock feces contain more nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. Nitrogen in human excreta is very volatile and should be collected and stored. The most common method of accumulation is composting with dirt, waste, weeds, etc. The ratio of composting is based on the principle that it can fully absorb excrement juice, and it can generally be mixed with soil or garbage that is 3 to 4 times the amount of excrement. Adding 3% to 5% of superphosphate to the excreta can reduce the loss of nitrogen and increase the availability of phosphorus. (10) Plant ash: Residues from the combustion of plant residues such as crop straw and firewood. Organic matter and nitrogen are all burned out during the combustion process, so they contain no organic matter and nitrogen and contain elements such as phosphorus, potassium, and calcium. The potassium contained therein is mostly water-soluble and can be directly absorbed and utilized by fruit trees. Dry grass ash should be accumulated, pay attention to moisture and waterproof, so as not to lose fertilizer. Plant ash should not be mixed with decomposed manure, human waste or ammonium sulfate and other acidic fertilizers (it can be used). In addition to saline and alkaline land, the soil can be used in general and can be used as base fertilizer or top dressing. 2. Commodity Fertilizer Commodity fertilizer refers to the fertilizer that is managed by the national fertilizer department and sold in the form of commodities in accordance with national regulations. Including commodity organic fertilizers, humic acid fertilizers, microbial fertilizers, organic compound fertilizers, inorganic (mineral) fertilizers and foliar fertilizers. (1) Commercial Organic Fertilizers: Commercial fertilizers made from a large number of animal and plant residues, excreta, and other biological wastes. (2) Humic Acid Fertilizers: Fertilizers containing peat (charcoal), lignite, and weathered coal containing humic acids are processed to produce fertilizers containing plant nutrients. (3) Microbial fertilizers: Live microbiological preparations produced by culturing specific microbial strains. According to microbial fertilizers to improve the different elements of plant nutrition, can be divided into five categories: rhizobia fertilizer, nitrogen-fixing bacteria fertilizer, phosphorus bacteria fertilizer, silicate bacteria fertilizer, compound microbial fertilizer. (4) Organic Compound Fertilizer: Fertilizer made by adding appropriate amount of micronutrient elements to livestock and poultry manure and other biological waste after detoxification treatment. (5) Inorganic (mineral) materials: The minerals are produced by physical or chemical industries, and the nutrients are in the form of inorganic salts, including mineral potassium and potassium sulfate, mineral phosphate (mineral phosphate), calcined phosphate (calcium, magnesium phosphate fertilizer, Defluorinated phosphate fertilizer), lime, gypsum, sulfur and so on. (6) Foliar fertilizer: Fertilizer sprayed on the leaves of plants and can be absorbed and utilized. Foliar fertilizers must not contain chemically synthesized growth regulators, including foliar fertilizers containing trace elements and leaves containing plant growth supplements. Surface fertilizers and so on. (7) Organic and inorganic fertilizers (semi-organic fertilizers): Fertilizers obtained by mechanically mixing or chemically reacting organic and inorganic fertilizers. (8) Blended fertilizers: Fertilizers (except nitrate-based nitrogen fertilizers) are blended in certain proportions of organic fertilizers, microbial fertilizers, inorganic (mineral) fertilizers, and humic acid fertilizers and are mechanically mixed. 3. Other fertilizers refer to foods that do not contain toxic substances, organic by-products of the textile industry, and organic fertilizers made from organic materials such as bone meal, bone glue residue, amino acid residues, poultry livestock processing waste, and sugar factory waste, and are approved for use by the agricultural sector. (b) Prohibited fertilizers 1. Municipal waste that is not harmlessly disposed or garbage containing metal, rubber, and harmful substances. 2. Nitrate nitrogen and unfamed human waste. 3. Unapproved fertilizer products. Second, the fertilization method (a) early application of multiple base fertilizer Most of the current orchard organic matter is less than 1%, some orchards even below 0.5%, far below the requirements of high-quality and high-yield gardens, so you must increase the amount of basal fertilizer. If the simultaneous consideration of the dual needs of tree growth and soil improvement, the application rate of organic fertilizer should be in the standard of two pounds to three pounds of manure. Therefore, a middle- orchard with a yield of 1,500 kilograms per mu should not be less than 3,000 kilograms of organic fertilizer. The most suitable period for Shiji is autumn (1 month before defoliation), followed by defoliation to pre-freezing, and thawing to pre-germination in the spring. The autumn basal fertilizer can have enough time to decompose and cause new roots to heal and heal roots. Therefore, it is the peak period of root growth and the strong root absorption. After absorption, it can increase the storage nutrition level of the tree and promote flower buds. The development is substantial. The higher nutrient reserve of the tree and the timely supply of nutrients in the soil in the early spring can meet the needs of sprouting, flowering, fruit setting and shoot growth in the spring. After the deciduous period and the base fertilizer in the spring, the effect of the fertilizer effect is late, and the effect on the early spring growth and development of the fruit tree is very small. When a large amount of fertilizer is absorbed and utilized, it often reaches the peak of the new shoot. In orchards with arid and water-free conditions in mountainous areas, basal fertilizers can also be applied during the rainy season because the basal fertilizer cannot be used immediately. However, organic manure must be a fully cooked manure, and the rate of fertilization should be fast, and care should be taken not to hurt the rough roots. When the source of organic fertilizer is insufficient, on the one hand, straw weeds can be used as a supplement to mix with organic fertilizers. On the other hand, the limited organic fertilizers should follow the principle of ensuring local distribution and ensuring the centralized distribution of roots. In order to give full play to the fertilizer effect of organic fertilizer. Concentrating on acupuncture points is to dig deep from the edge of the canopy to a depth of 50 cm and a diameter of 30 cm to 40 cm. The number of fertilizers depends on the amount of fertilizer, and then the organic fertilizer and soil are mixed with 1:3 or some straw. Fill in the hole and water again. In addition, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers and even zinc fertilizers and iron fertilizers can be mixed with organic fertilizers to increase their utilization. (B) a reasonable top dressing 1. Appropriate application of nitrogen fertilizer: nitrogen is the basis of fruit tree growth and results. Within a certain limit, adding nitrogen fertilizer can significantly improve the photosynthetic performance of leaves, and increase tree vigor and yield. However, exceeding the limit can easily lead to prosperous foliage, difficulty in flowering, and fruit quality decline. And after a large amount of nitrogen (usually in the irrigation of large water after fertilizer) due to the limited absorption capacity of the root system, excess nutrients will be leaching loss, resulting in a great waste of fertilizer, and even a large amount of fertilizer application occurs. Therefore, while emphasizing the increase of investment in orchards, it is also necessary to take into account the needs of the trees and the benefits of fertilization. Do not blindly invest a lot. The appropriate amount of nitrogen fertilizer should be determined based on comprehensive consideration of soil fertility, fertilizer holding capacity and tree type, generally 1 year to 2 years, each cultivable can recover urea 50 grams to 100 grams, 3 years to 4 years old tree 150 200 grams, after 5 to 6 years, the trees that enter the fruiting period, because they are mostly planted in close-packed small crowns, and there are more than 50 planted acres, and the density varies greatly, so the size and load of the single tree Different amounts, it is not appropriate to calculate the amount of fertilization per plant, generally not more than 15 kilograms of urea per acre per crop, the amount of urea per acre of 30 kg to 45 kg per year. 2. Nitrogen chasing from the ground: Under the condition of insufficient organic matter, appropriate recovery of nitrogen fertilizers on barren land can significantly improve the photosynthetic performance of leaves, thus increasing the accumulation level of photosynthetic products of trees and playing a role in “carbon addition by nitrogenâ€. . The accumulation of photosynthetic products in turn promotes the growth of the root system and increases the absorption capacity of the root system. Barely thin trees, flower buds are difficult to form, etc. are related to the level of carbon and nitrogen metabolism of plants. Therefore, an appropriate increase in the amount of nitrogen fertilizer, nitrogen carbon, nitrogen fertilization is an effective measure to produce trees and flowers in the orchard. The topdressing methods for different soils are also different. After the spring nitrogen topdressing, the fertilizer usually starts to function from 10 days to 15 days, generally 5 days to 7 days in summer, and between autumn and autumn, which is mainly related to the level of soil organic matter and adsorption capacity. After 20 days of topdressing (high temperature season), the fertilizer effect is less pronounced. Low levels of organic matter, poor fertility, poor protection of the mountains and sand, nutrient leaching with water is serious, the effective period of fertilizer is shorter, and often in July to August the rainy season caused soil denitrification. Therefore, topdressing in mountain sand should be applied sparingly, and it is better to use nutrients in the water to penetrate the concentrated distribution layer of the root system. After the rainy season, a small amount of topdressing nitrogen fertilizer can be used to make up for leaching losses. In soils with higher salinity, when the pH value is more than 7.5, the available phosphorus content in the soil is generally low, and fruit trees are often not susceptible to flowering due to phosphorus deficiency. This type of soil chases phosphate fertilizers ( Top dressing or top dressing is an indispensable part of early fruiting and high-yielding topdressing. Phosphorus topdressing in the soil is easily fixed. Therefore, it is advisable to mix it with high-quality organic fertilizers rich in nutrients. 3. Because of tree topdressing: After nutrients are taken from the fruit tree roots, nutrient allocation is limited by the nutrition center, ie, nutrients are preferentially transported to the most active parts of the metabolism, and further promote the growth and development of this part. For example, if Xinwangwang grows fertilizer for a long time, the fertilizer will enter into the long shoots of the new shoots and will further promote the growth. After the shoots have stopped, the central advantage of the prosperous part will weaken or disappear, and the difference in nutrients from topdressing to various organs will decrease. The distribution is relatively balanced, and the auxiliary effects of the weak parts (such as short branches) on the canopy are relatively large, which is conducive to the differentiation of buds. Therefore, different tree growth, different flower and fruit, the purpose of fertilization is different, so the fertilization period should not be the same, fertilization must be combined with plant type. Weakly growing trees, including “small old treesâ€, should be used to increase the supply of nutrients in order to enhance the growth of branches and leaves. It is best to grow fertilizers in the early and the Shoot growth, weak branches stronger. The trees that grow energetically but have little flowers or grow inefficiently, in order to ease the overgrowth of branches and leaves, and promote the differentiation of short shoots, should avoid long-term growth and top-dressing after new shoots are stopped. Among them, the main long-term (August and early September) should be mainly for the autumn shoots, and the long-term (June and mid-June) should be supplemented by the spring shoots. When the spring shoots are stopped for a long time and the topdressing nitrogen fertilizer is applied, the water should not be too large, so as not to stimulate the growth of the shoots too early. The type of fertilization should also be adjusted for tree conditions. Practice has proved that nitrogen fertilizer helps the growth of branches and leaves obvious, and weak branches rejuvenate more with some nitrogen fertilizer. Phosphorus and potassium fertilizers have the effect of alleviating over-proliferation, and it is advisable to increase the amount of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers for the unproductive trees and to reduce the amount of nitrogen fertilizers. The top dressing is best applied to the tree trays. Immediately, gently poke, mix the fertilizer, and then water. When the tree plate is covered with grass, it can be directly applied to the grass and then washed down with water; or a corner of the cover grass can be sprinkled on the soil surface, and then the water can be washed down and the grass can be covered. (3) Fertilizer outside roots Fertilizing fruit trees outside the roots of the tree is to spray the fertilizer directly on the branches and leaves of the tree, which can make up for the lack of root absorption or as an emergency measure. Spraying fertilizers outside the roots is not affected by the number of new roots and the physical and chemical characteristics of the soil. Directly entering the branches and leaves will help change the nutritional status of the tree more quickly. Moreover, after top dressing, the distribution of nutrients is not limited by the growth center, and the distribution is balanced, which is conducive to the relaxation of the tree potential and the strengthening of the weak parts. In addition, top-dressing fertilizers are often used for the correction of zinc deficiency, iron deficiency, boron deficiency, and compound fertilizers. However, the root-spraying fertilizer cannot replace the rhizosphere topdressing fertilizer. The two have their own characteristics and should complement each other. From 10 days to 15 days after the root-spraying, the response of the leaves to the fertilizer element is the most obvious, and gradually decreases afterwards. It disappears from the 25th to the 30th day. Therefore, if you want to play a role in a critical period, separate the leaves in this period. Sprayed continuously for 15 days. After harvesting in autumn, before defoliation and before sprouting in early spring, it is an important period for extra-root fertilizer application. In particular, in Dainian trees and early deciduous trees, due to the small number of new roots in autumn and early spring in the following year, the uptake of soil topdressing is limited. Therefore, the spraying of urea leaf stems in autumn can compensate for the lack of storage nutrients and the absorption of root systems in early spring. A series of growth and development in the spring are very favorable, the flower organs are well developed, the fruit setting rate is high, and the short branches are thick. In addition, zinc, boron and other elements of the lack of correction should also pay attention to the two key periods in the fall and early spring, these two spray correction is generally better than the growth season.
Boob tape, breast lift tape
Boob tape is based on 95% cotton and 5% Elastic Spandex fabric. The material is safe, soft, breathable, which makes you comfortable in it. It has super strong elasticity, lateral stretching is more than 230%. It is coated with imported wave pattern glue, which ensures the tape has stable adhesion and easy to remove, do not hurt your skin. It has a certain waterproof effect, the adhesion will not be reduced even you are sweaty or swimming. It has wonderful lifting and gathering effect, let you have a proud chest curve.
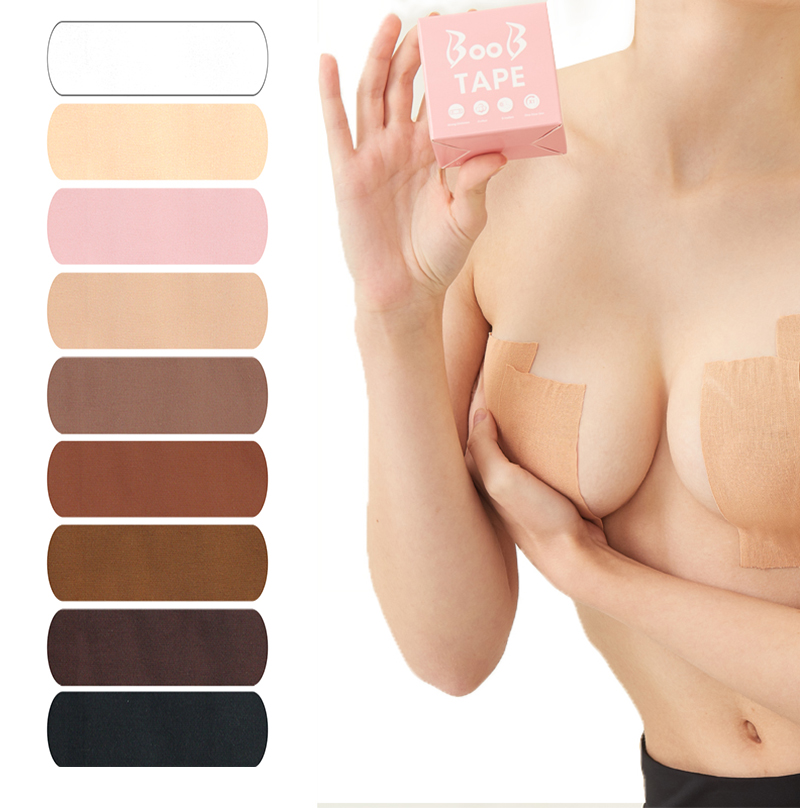

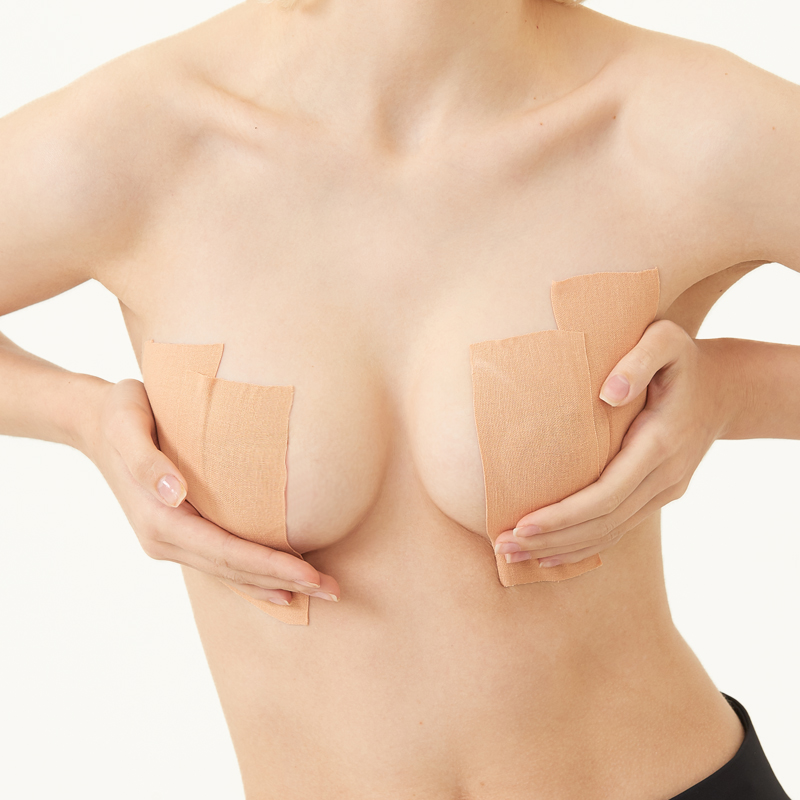
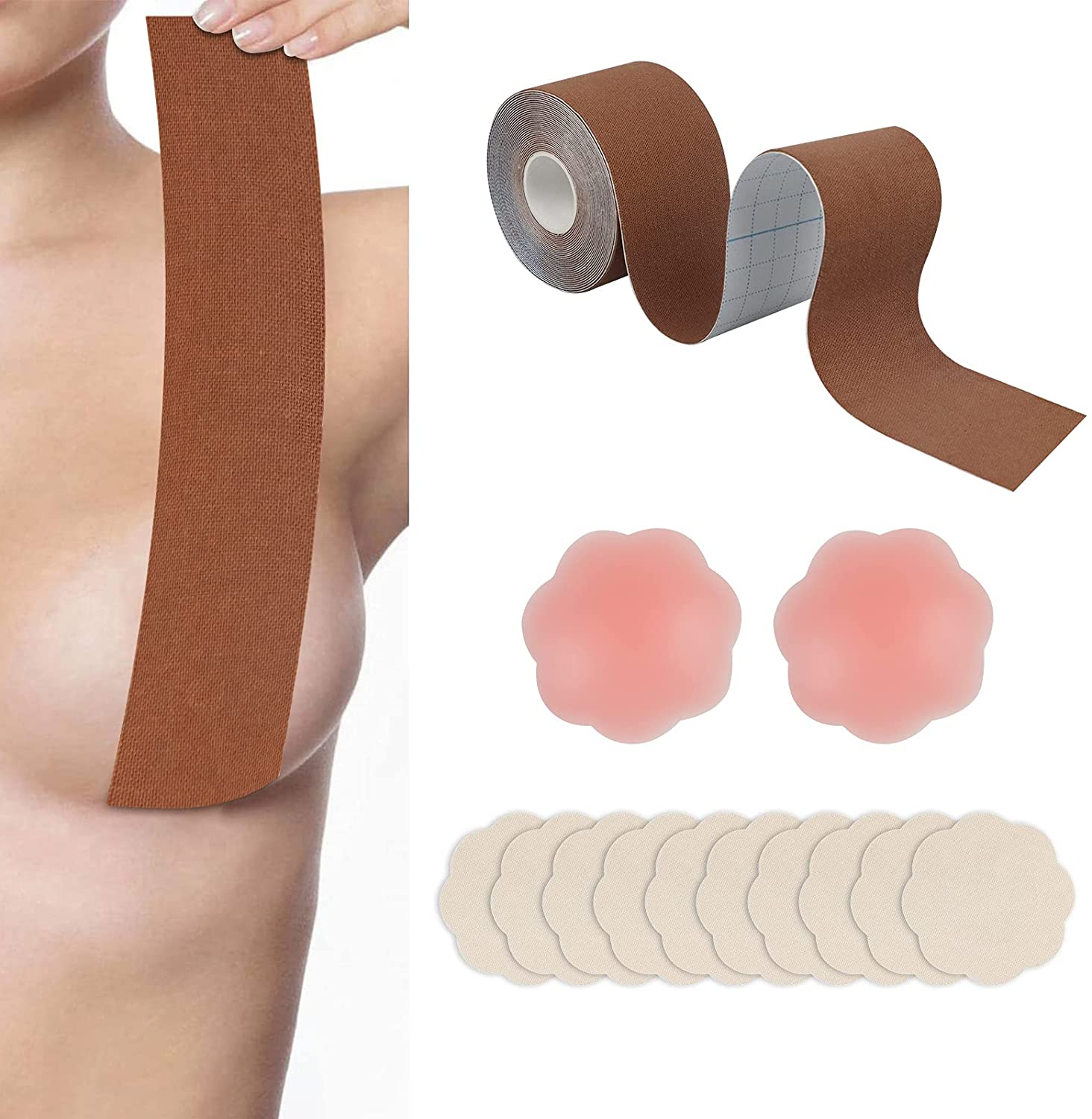
boob tape,breast lift tape,boob tape and nipple cover,boob lift tape,breast tape
Kunshan Jieyudeng Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.jerrytape.com