Brain cell acid-base imbalance or senile dementia This study identified potential drug targets
Brain cell acid-base imbalance or senile dementia This study identified potential drug targets
August 09, 2018 Source: Chinese Journal of Science and Technology
Window._bd_share_config={ "common":{ "bdSnsKey":{ },"bdText":"","bdMini":"2","bdMiniList":false,"bdPic":"","bdStyle":" 0","bdSize":"16"},"share":{ }};with(document)0[(getElementsByTagName('head')[0]||body).appendChild(createElement('script')) .src='http://bdimg.share.baidu.com/static/api/js/share.js?v=89860593.js?cdnversion='+~(-new Date()/36e5)];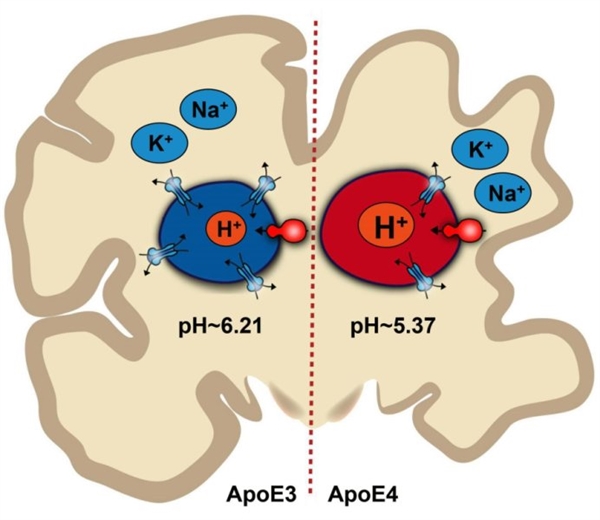
An imbalance in the pH of brain cells can lead to Alzheimer's disease. Image source: Johns Hopkins University
US scientists have said that they have found new evidence in mouse brain cells called astrocytes cultured in the laboratory, suggesting that one cause of Alzheimer's disease may be simple intracellular bodies. Acid-base (or pH) chemical imbalance. Endosomes are structures that transport nutrients and chemicals within cells.
Astrocytes remove the so-called beta amyloid from the space between neurons, and decades of research evidence suggests that if there is a problem with the clearance process, amyloid will accumulate around the neurons and cause Characteristic amyloid plaques and neuronal degeneration, which are hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease that destroys memory.
The new study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, said that scientists have used drugs called histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors for genetic engineering through common Alzheimer's disease genetic variants. The pH of the mouse cells was unbalanced, and the experiment successfully reversed the pH and improved the ability to clear amyloid beta.
HDAC inhibitors are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of certain types of blood cancer patients, but not for Alzheimer's patients, and most HDAC inhibitors do not cross the blood-brain barrier. Scientists are planning further experiments to determine whether HDAC inhibitors have similar effects in human astrocytes in laboratory-cultured Alzheimer's patients, and have the potential to design HDAC inhibition across the blood-brain barrier. Agent.
Rajini Rao, a professor of physiology at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, said: "When Alzheimer's disease is diagnosed, most of the nerve damage has already occurred. It may be too late to reverse the disease. This is why we need to pay attention to the earliest pathological symptoms of the disease or markers of Alzheimer's disease. We already know that the biological and chemical characteristics of endosomes are an important factor that occurs very early before cognition begins to decline. ."
About 20 years ago, scientists at the school and New York University found that in the brain cells of patients who eventually develop Alzheimer's disease, the intracellular bodies (the circular compartments that carry the "goods" inside the cells) become more Large, its number in the cell also becomes more, suggesting that problems with intracellular bodies may lead to the accumulation of amyloid in the space around the neurons.
In order to transport "goods" from one place to another, the endosomes use chaperone proteins (which can bind to specific "goods" and transport them back and forth from the cell surface). Whether or not this binding will occur and how it occurs depends on whether the intracellular body is at an appropriate pH level (a delicate balance of acid and base). Appropriate pH levels allow the endosomes to float to the cell surface and then return to the interior of the cell.
A protein capable of transporting charged hydrogen atoms (protons) into and out of the endosome is embedded in the membrane of the endosome, and the number of protons inside the intracellular body determines its pH.
When the liquid in the endosome becomes too acidic, the "goods" will be trapped in the endosome that stays deep in the cell, and when the contents of the endosome are more alkaline, the "goods" will The cell surface stays for an extended period of time.
To help determine whether this pH imbalance will occur in Alzheimer's disease, Johns Hopkins graduate student Hari Prasad retrieved a large body of scientific literature on Alzheimer's disease to find and normal In comparison to humans, genes that are downregulated are expressed in the brain of the patient. Eventually he found that 10 of the 100 most frequently down-regulated genes were associated with proton flux in the cell.
In another group of brain tissue samples, the expression of NHE6 (which is responsible for proton transport of the endosomes) was reduced by about 50% in Alzheimer's patients.
To measure the pH balance in the endosomes without destroying astrocytes, Prasad and Rao used pH-sensitive probes in the experiment that were absorbed by the endosomes and luminesed based on different pH levels. They found that mouse cell lines containing Alzheimer's disease variants have more acidic endosomes.
"If there is no normal functioning of NHE6, the intracellular bodies will become too acidic and will stay inside the astrocytes, thus avoiding their responsibility to clear beta amyloid," Rao said.
The researchers also found that a protein called LRP1 captures amyloid outside the astrocyte and delivers it to the endosome. On the surface of mouse astrocytes cultured in the laboratory, the protein contains a human genetic variant called APOE4, which is commonly associated with Alzheimer's disease.
The researchers tested nine different types of HDAC inhibitors on cell cultures of mouse astrocytes engineered with APOE4 gene variants. The results indicate that a broad spectrum HDAC inhibitor can increase NHE6 expression to levels comparable to mouse astrocytes that do not have Alzheimer's disease gene variants. They found that HDAC inhibitors can alter the pH imbalance in the endosome and restore LRP1 to the astrocyte surface, effectively removing beta amyloid. (Zhao Xixi)
Related paper information: http://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1801612115
Chinese Journal of Science (2018-08-07 2nd Edition International)
Feature:
1. Made of high‑quality nitrile rubber material, which has excellent wear resistance and long service life.
2. The non‑slip texture on the surface provides ideal grip in dry and oily environments.
3. The interior of the gloves is made of cotton flocking, which provides users with a comfortable hand touch.
4. It can be widely used in agriculture and gardening, metal processing, pesticide industry, petroleum and gasoline refineries, etc.
5. The anti-permeability level of chemicals such as n-heptane, sodium hydroxide and concentrated sulfuric acid reaches level 2 or above (30 minutes), suitable for immersion operation.
Specification:
Item Type: Gloves
Material: Nitrile Rubber + Cotton Flocking
Uses: Agriculture and gardening/metal processing/peroxide/pesticide industry/petroleum and gasoline refineries/automotive and supply industries
Function: Protection from saturated hydrocarbons/inorganic bases/organic bases/inorganic acids


Industrial Gloves,Construction Gloves,Construction Work Gloves,Industrial Nitrile Gloves
Jiangsu Asbao Medical Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.iigloves.com