CircRNA recurrence IF=18.88 high score article--Circle mechanism research summary
Article introduction
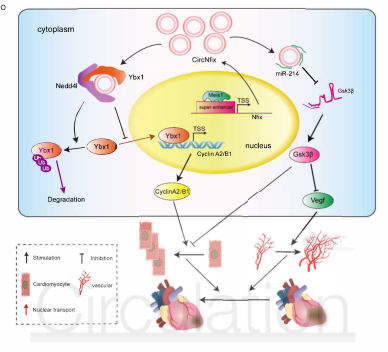
CircRNAs are becoming potent regulators of heart development and disease, but their role in cardiac regeneration remains unknown. In view of this, the author and his team explored the function of circRNA-Nfix associated with super-enhancer (SEs) in the post-myocardial infarction regeneration in mice, and explored its molecular mechanism of regulating cardiac remodeling, and in 2019 On April 5, the results were published in the circulation magazine (IF=18.88). In this study, the authors first used bioinformatics to analyze RNA sequencing data and combined SE catalogues to identify SE-related circRNAs, and used qPCR and in situ hybridization techniques to detect the discovery of circNfix in human, rat, and mouse adult hearts. Overexpression. Then, by interfering with or overexpressing circNfix in myocardial cells (CM) after myocardial infarction (MI), its role in cell proliferation and myocardial repair was explored, and it was found that down-regulation of circNfix can promote CM proliferation and angiogenesis after myocardial infarction, and Inhibit CM apoptosis, reduce cardiac dysfunction, and improve prognosis. Finally, the authors used chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSAs) to determine the transcription factor Meis1 binding to SE with circ-nfix; RNA pull-down and luciferase reporter assays for circRNA Interaction with proteins or with miRNAs; found that down-regulation of circNfix enhances the interaction of Ybx1 with Nedd4l (E3 ubiquitin ligase) and induces ubiquitination of Ybx1, inhibiting the expression of downstream cyclin-A2 and cyclin-B1. In addition, circNfix also acts as a ceRNA, adsorbs mir-214 and promotes Gsk3β expression and inhibits β-catenin activity. That is, SE-regulated circNfix deletion may inhibit the Ybx1 ubiquitin-dependent degradation, increase miR-214 activity, promote cardiac regeneration and functional recovery after myocardial infarction, and may be a promising strategy to improve the prognosis of myocardial infarction.
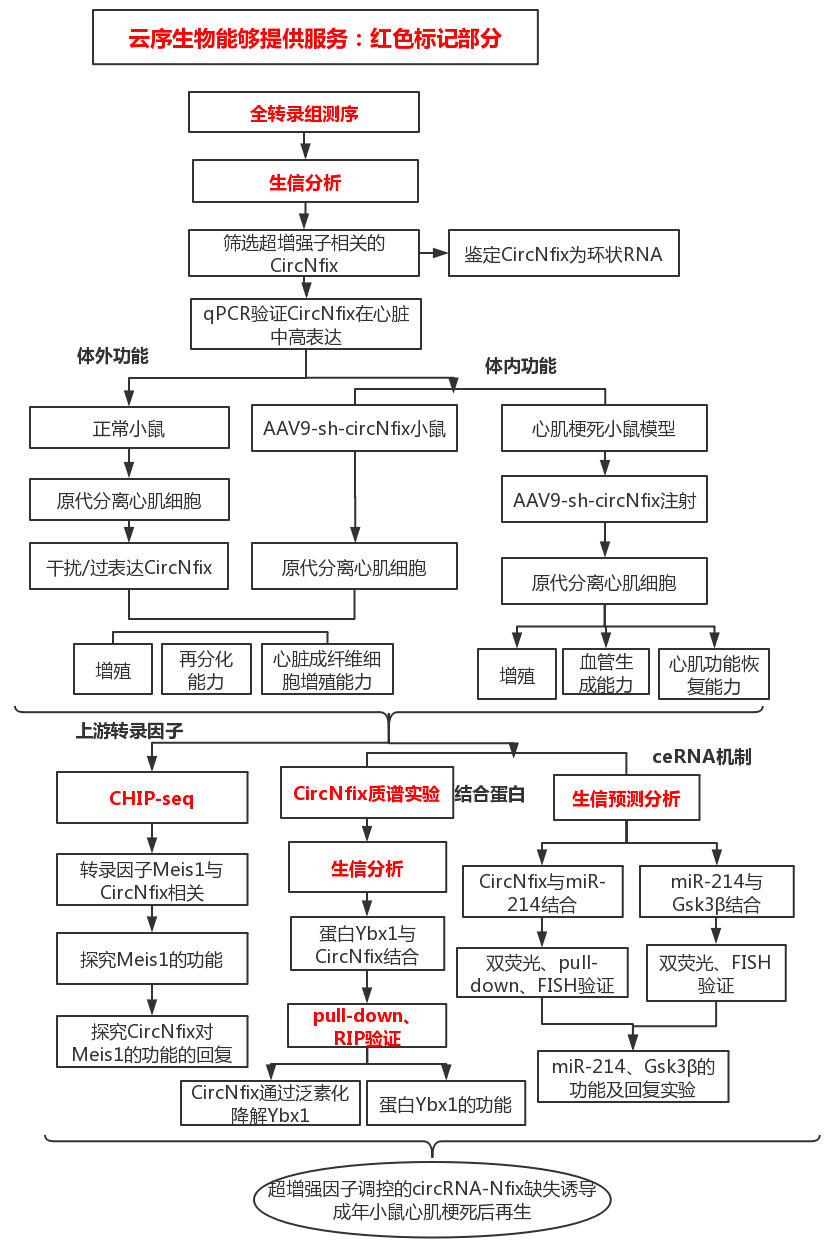
Technical route
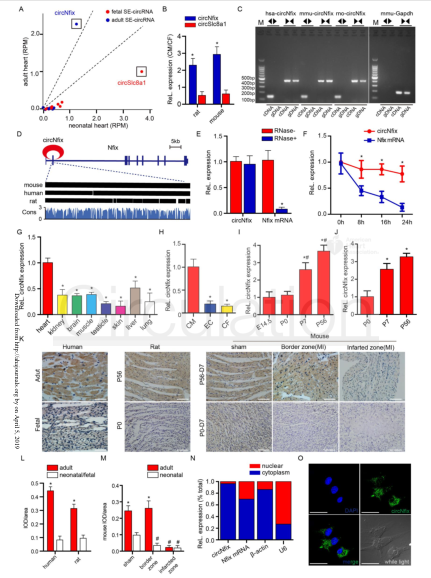
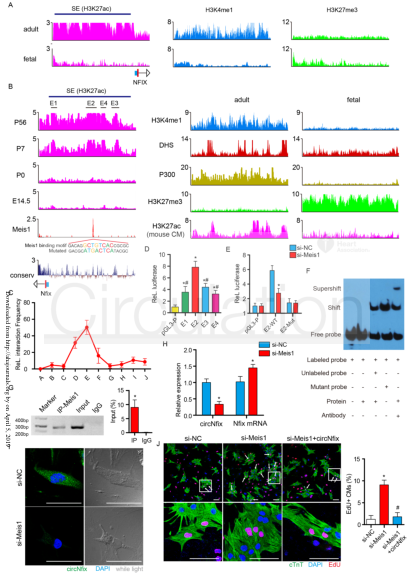
(1) The transcription factor Meis1 drives circNfix expression by SE binding to the Nfix site: ChIP-seq spectra of H3k27ac, H3k4me1 and H3k27me3 at the Nfix site of human cardiac tissue (the cloud sequence organism provides this service) (A). Conservative scores of H3k27ac, H3k4me1, H3k27me3, P300, DNA hypersensitivity (DHS), Meis1 and PhastCons in the Nfix site of mouse cardiac tissue, and H3k27ac ChIP-seq in mouse CMs (the cloud order organism provides this service) (B ). 3C-qPCR analysis of the looping event between SE and circNfix promoter region (C). The pgl3 promoter reporter vector luciferase assay (D) constructed with four component enhancers (E1, E2, E3, E4). Luciferase activity (E) of wild-type E2 and mutant E2 in P7 CMs after Meis1 silencing. EMSA results (F) of nuclear proteins extracted from P7 CMs after incubation of the Meis1 binding site in circNfix-SE by DIG-ddUTP-labeled oligonucleotide probes. ChIP-qPCR (provided by the cloud-sequence organism) assay showed that the Meis1 binding site was amplified in circNfix-SE (G). QRT-PCR was used to detect the expression levels of circNfix and Nfix mRNA in P7 CMs after Meis1 gene knockout (H). RNA FISH was used to detect the subcellular localization of circNfix in P7 CMs after Meis1 knockout (I). EdU staining was used to detect the effect of Meis1 and circNfix interference on the proliferation of P7 CMs (J).
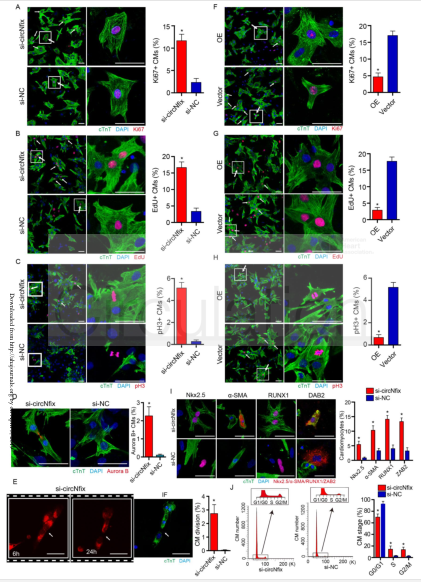
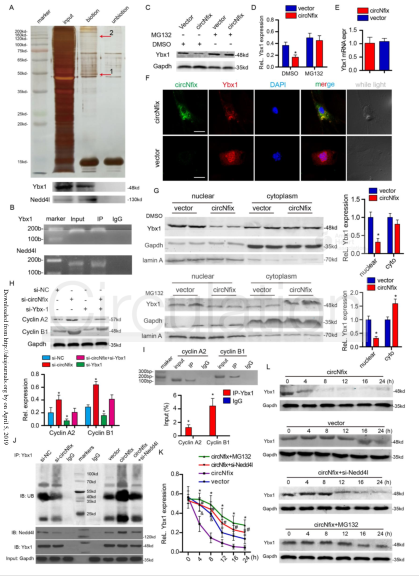
(2) CircNfix binds to Ybx1 and promotes its degradation: protein profiling of circNfix and control (A). RIP experiments were performed using Ybx1, Nedd4l or negative IgG antibodies (cloud order organisms provide this service) (B). Ybx1 protein expression level (CD) after overexpression of circNfix in P0 CMs. qRT-PCR was used to detect Ybx1 mRNA expression level (E) in P0 CMs. Subcellular colocalization of circNfix and Ybx1 (F) when RNA FISH overexpresses and does not express circNfix in P0 CMs. Fractionation experiments showed that circNfix overexpression promoted the translocation of Ybx1 in the cytoplasm and increased the degradation of Ybx1 in the cytoplasm (G). Expression levels of cyclin A2 and cyclin B1 after circNfix and Ybx1 interference (H). ChIP-qPCR (provided by the cloud-sequence organism) assay showed amplification of the Ybx1 binding site in the cyclin A2 and cyclin B1 promoters (I). The cell lysate was immunoprecipitated with an anti-Ybx1 antibody, and subjected to WB analysis by immunoblot analysis using a ubiquitin (Ub)-specific antibody, an anti-Ybx1 antibody or an anti-nedd4l antibody. Ybx1 protein expression level (KL) in CMs overexpressing circNfix.
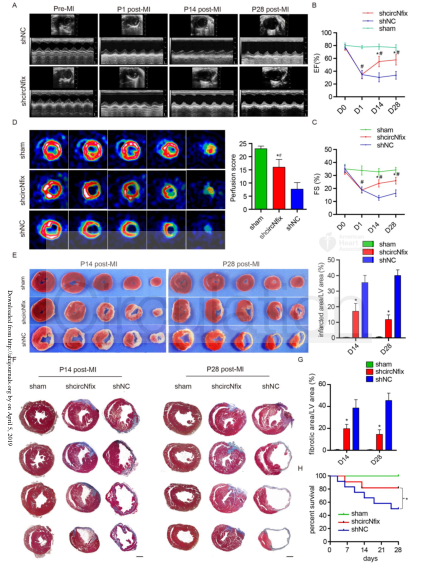
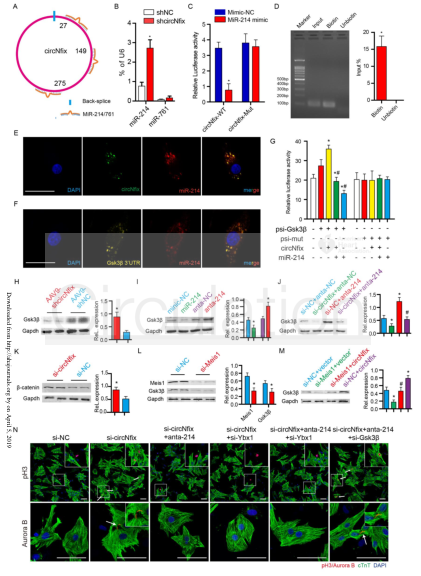
(3) Interaction of circNfix with miR-214: miR-214 and miR-761 were predicted to bind to circNfix (A). Expression of miR-214 and miR-761 after down-regulation of circNfix in adult mouse hearts (B). The dual fluorescence reporter assay detects that miR-214 and circNfix can bind directly (C). RNA pull-down (the cloud sequencing organism provides this service) experiments to detect circNfix can pull down miR-214 (D). In RNA FISH assays, miR-124 and circNfix were colocalized in the cytoplasm (E) in P0 CMs. In RNA FISH assays, miR-124 and Gsk3β were colocalized in the cytoplasm (F) in P0 CMs. The dual fluorescence reporter assay detects direct binding (G) of miR-214 and Gsk3β 3'UTR. WB detects the expression level of Gsk3β protein after interference with circNfix (H). WB detects the expression level of Gsk3β protein after interference or overexpression of miR-124 (I). WB detects the expression level of Gsk3β protein after interference with circNfix and miR-214 (J). In CMs, the expression level of β-catenin after circ Nfix was disturbed (K). In CMs, the expression level of Meis1 and Gsk3β after Meis1 was interfered (L). In CMs, the expression level of GSK3β (M) after interference with Meis1 and circNfix. After interference with circNfix, Ybx1, miR-214 and Gsk3β, P7 CMs were subjected to pH3 and Aurora B immunostaining (N).
https://
RNA pull down
RIP sequencing
ChIP sequencing
M6A RNA whole transcriptome methylation sequencing
m6A RNA circular RNA sequencing
M5C RNA whole transcriptome methylation sequencing
m5C RNA circular RNA sequencing
m1A RNA whole transcriptome methylation sequencing
m1A RNA circular RNA sequencing ultra-micro circular RNA methylation sequencing
1.Whole-genome and Transcriptome Sequencing of Prostate Cancer Identify New Genetic Alterations Driving Disease Progression
2.SUMOylation of the m6A-RNA methyltransferase METTL3 modulates its function
3.CircHLA-C Plays an Important Role in Lupus Nephritis by Sponging miR-150
4.Identification of Circular RNAs and Their Targets in Leaves of Triticum aestivum L. under Dehydration Stress
5.Circular RNA alterations are involved in resistance to avian leukosis virus subgroup-J-induced tumor formation in chickens
6.Identification of circular RNAs and their alterations involved in developing male Xenopus laevis chronically exposed to atrazine
7.Identification and characterization of circular RNAs in zebrafish
8.Differential Expression of Circular RNAs in Glioblastoma Multiforme and Its Correlationwith Prognosis
9.Circular RNA Signature Predicts Gemcitabine Resistance of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcino
10.Circular RNA Vav3 sponges gga-miR-375 to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition
11.RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
12.Analysis of changes to lncRNAs and their target mRNAs in murine jejunum after radiation treatment
13.circular RNA expression alteration in exosomes from the brain extracellular space after traumatic brain injury in mice
Shanghai Cloud-seq Biotech Co., Ltd.
Address: 3rd Floor, Building 20, No. 518, Zhangzhu Road, Songjiang District, Shanghai

Telephone Fax Website:
mailbox:
X Ray Single Side Protection Lead Apron,Xray Radiation Lead Aprons,X-Ray Front Protection Lead Apron,X Ray Radiation Proof Lead Apron
Longkou Kangxie Medical Instrument Co., Ltd , https://www.lkkangxiemedical.com