Process related to microbial strain management
1.1 Collection of strains
The first strains used in the laboratory are purchased from the national statutory body, the second is the purchase of commercial derivative strains, and the third is the exchange of strains in scientific research. No matter which source, it is unified. The collection is carried out in strict accordance with the specifications. Requires reliable packaging, rapid collection, no leakage and no pollution. Ensure that the strain is qualified and environmentally safe. There should be a species identification in the collection. Qualified suppliers of qualified standard strains are selected. Each batch of standard strains must be accompanied by a supplier's certificate or test report or instructions to prove that the standard strain purchased is qualified.
1.2 standard strains and acceptance
When the laboratory receives the standard strain, it should first be tested in accordance with the sexy officer, record the strain number and the source route of the standard strain to ensure traceability. The name and quantity of the standard strain, the date of manufacture, the date of receipt, and the presence or absence of damage should also be recorded.
1.3 Resuscitation of freeze-dried standard strains
1.3.1 Open the product packaging: first wipe the outer packaging with 70% alcohol cotton, then open it.
1.3.2 Resurrection: Select the appropriate medium and culture conditions (according to the instructions for use of the strain, see Appendix) for resurrection. The first activation of the strain is preferably on a non-selective agar medium, and liquid medium is generally not used unless otherwise specified or recommended. The passage number of the freeze-dried strain shall not exceed 5 generations, and the freeze-dried standard strain purchased from the standard strain collection center is the F0 generation.

Appendix freeze-dried bacteria cultures recovery and preservation passage
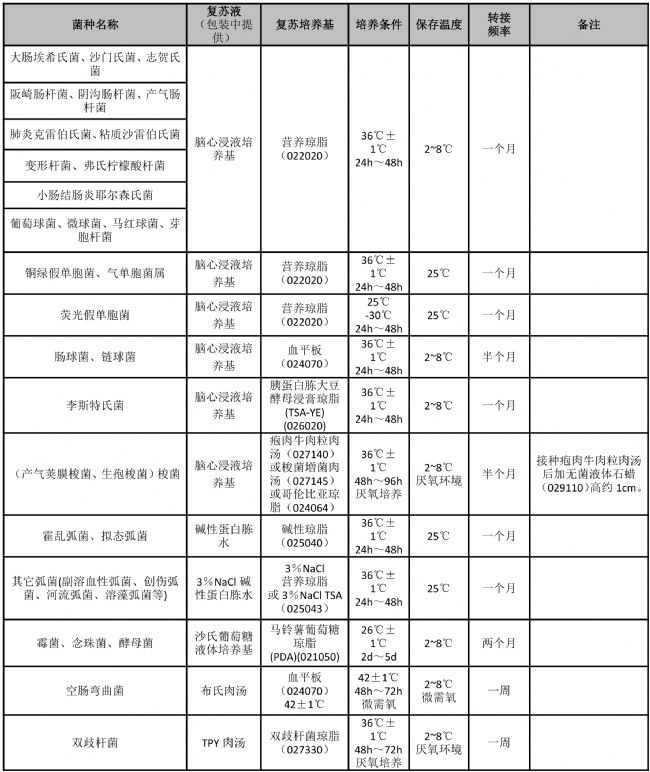
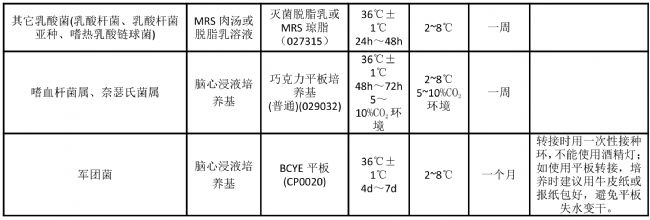
Note: The number behind the culture medium is the product number of Guangdong Huan Kai Microbiological Co., Ltd. If you need to purchase, please contact the dealer or salesman. The above table provides a method for short-term preservation of strains for reference.
1.4 Working methods and methods for confirming working strains
The above cultures are aseptically inoculated, and individual colonies are isolated on the corresponding medium plates (nutrient agar, soybean tryptone agar) or corresponding bacterial identification plates (eg, ihongmeilan, MacKangkai, BP, etc.). , culture under suitable conditions (if the microorganisms are anaerobic bacteria, the culture conditions should be anaerobic conditions). Take the fungus and yeast to SDA (Sabro medium) plate or rose red sodium culture in the same way. The substrate was cultured for 7 days at 23-28 ° C; after culture, it was observed whether it had a typical colony state, and then a single pure colony was picked, subjected to Gram staining and microscopic examination, and the staining characteristics and cell morphology were observed to confirm the strain.
1.5 Pollution treatment
If other colonies are found on the plate, the operation is contaminated or the strain is impure. Want to
The contaminated culture is sterilized, the cause is sought, and the pure colonies are re-isolated.
1.6 strain preservation
All strains are kept in a dedicated refrigerator or other storage method by a laboratory person (double double lock). It is necessary to establish a strain registration account, and record the collection, storage, preparation, use and disposal of the strains in detail; each strain must have a test and identification report (the specific identification method can be found in the method of the strain quality identification certificate). );
The specific strain preservation method is generally:
The broth after resuscitation and the sterilized glycerin were mixed at a ratio of 15% glycerin (broth 8.5 mL + glycerol 1.5 mL), frozen at -30 °C, (can be stored in 2 mL cryotubes), as a reserve strain F1, Commercially available strain preservation tubes can also be used.
Passage of 1.7 strains
1.7.1 Recovery of standard strains:
1 The operation of the strain should be carried out under aseptic conditions to prevent contamination of the bacteria.
2 Simply use the beads to roll on the plate or broth in each use and resuscitation.
1.7.2 Standard stock strains must be confirmed for each transfer. (The method of confirmation is generally their unique form, in the form of identification medium)
1.7.3 Method of transfer of working strains:
1. Prepare nutrient agar medium (Vibrio hemolyticus plus 3% sodium chloride), autoclave at 121 °C for 15 minutes, then pack in a test tube, cool and set aside.
2. Under aseptic conditions, pick the lawn moss from the inoculating loop to a fresh test tube and inoculate it in a “m†shape, and place it in an incubator at 36 ° C for 24 hours.
1.7.4 Use of working strains
1.7.4.1 Internal quality control: once a month, positive control, medium acceptance per batch;
1.7.4.2 External quality control: capability verification, laboratory comparison;
1.7.5 Period verification of working strains
Frequency of verification during 1.7.5.1: A semi-annual verification of the use of standard strains.
1.7.5.2 Method and basis for verification during working strain: same as confirmation of working strain.
1.7.5.3 Check records during the establishment of standard strains.
Identification and use period of 1.8 strains:
1.8.1 Identification: The calculation of the species algebra is the 0th generation of the dry powder species, and the transfer is performed once plus one generation. The specific identification is: the first generation of Listeria monocytogenes, the mark is DZ-0, the first generation mark is DZ-01, the first generation has 12, then DZ-01-01, ..., DZ-01- 12; and indicate the date: fill in as 2016.02.13.
1.9 Preservation of strains
1.9.1 Store the in-vitro strains in the refrigerator at 2~8 °C for storage.
1.9.2 Store the strains that have been passaged and cultured in a refrigerator at 2 to 8 °C. Each preserved strain must be marked with the name of the fungus, the standard number, the pass, and the date of passage.
1.10 species destruction
1.10.1 After the strain has been used or exceeds the storage period, it should be destroyed.
1.10.2 The strain to be destroyed shall be sterilized by high pressure steam (121 ° C) for 30 minutes.
After the 1.10.3 sterilization, it is cleaned and treated.
The species destroyed in 1.10.4 should be recorded. At the time of destruction, the person in charge of the inspection supervises the destruction, and the custodian is responsible for the destruction.
Organic Scholartree Fruits Extracts
Organic Scholartree Fruits Extracts,Scholar Tree Fruit Extracts,Scholartree Fruits Extracts,Scholartree Extract
Hengshui Shanzhi Health Drink Co., Ltd , https://www.grasspowder-sz.com