Summary of 46 new drugs approved by the FDA in 2017 and domestic progress
In 2017, the FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) approved 46 new drugs, including new drug entities (NMEs) and biologics license applications (BLAs) for new drug applications.
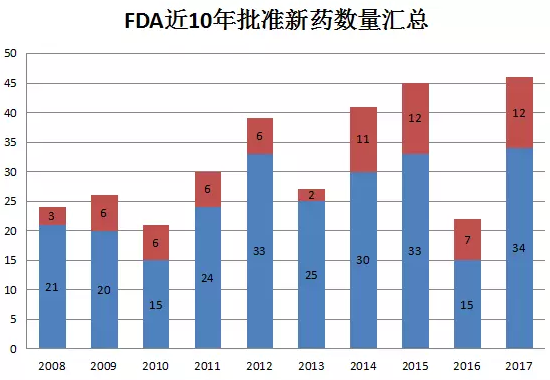
The picture above shows the number of new drugs approved by CDER each year in the past 10 years. In 2017, CDER approved a total of 46 new drugs, including 12 BLAs and 34 NMEs. Compared with 22 in 2016, this year is ideal, reaching the highest value of new drug approval in the past 10 years.
Rare OR "Orphan" Diseases)
Of the 46 new drugs approved, 18 new drugs were eligible for orphan drug (O), accounting for 39% of CDER-approved new drugs. Rare diseases have two characteristics, one is the small number of patients (the disease in the United States is less than 200,000; the EU is a disease of 5/10000); the second is a serious disease that is life-threatening and healthy.
Priority Review
If CDER determines that the drug has the potential to make a substantial boost to health care, the drug will receive a priority review. The drug was reviewed within 6 months instead of the standard 10 months. Twenty of the new drugs approved in 2017 were identified as priority reviews (P), accounting for 43.5% of 46 new drugs.
In addition, CDER applies a variety of regulatory methods to accelerate the development and approval of new drugs. In addition to the priority review, these methods include: Fast Track, Breakthrough, and Accelerated Approval.
In the field of treatment, 2017 is still relatively rich, but anti-tumor drugs are still the most, accounting for about 26%. On the whole, the US FDA is also the first choice for new drugs in various companies. The 46 new drugs have 35 drugs, which are the first in the world. At present, only some of these drugs have entered the clinical trial stage in China, and the government and domestic pharmaceutical companies need to work harder to get people to get the latest drug treatment.
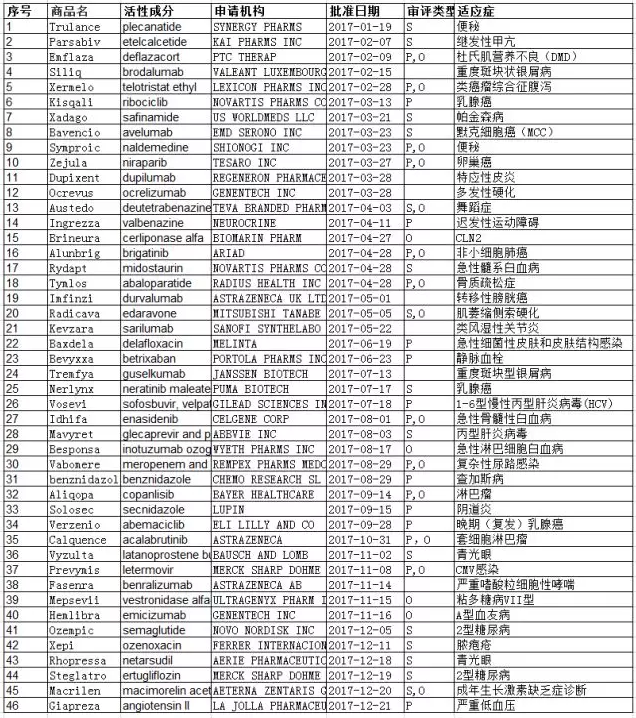
The chart below shows a summary of 46 new drugs approved in 2017, from the FDA website, Novel Drug Approvals for 2017.
01 Trulance (Plainide)
On January 19, 2017, the FDA approved Trulance (plecanatide) developed by Synergy Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC) in adult patients. This product is the first new drug approved by the FDA in 2017.
In two 12-week, placebo-controlled clinical trials, a total of 1,775 adults participated to determine the safety and efficacy of Trulance. Subjects were those who had been diagnosed with constipation for at least 6 months and had less than three bowel movements per week for the first three months with constipation symptoms. They need to be given a placebo or Trulance randomly once a day. It was found that the Trulance group was more likely to experience complete spontaneous bowel movements than the placebo group, and the frequency, consistency, and deformability of the feces were also improved.
02 Parsabiv (Etelcalcetide)
On February 7, 2017, the FDA approved Amgen's Parsabiv (Etelcalcetide) for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in adult patients with hemodialysis chronic kidney disease (CKD). Earlier, Anjin submitted the drug application to the FDA in August 2015, but was rejected. In Europe, Parsabiv was approved for the same indication in November 2016. In 2 randomized, double-blind, phase III controlled trials, 1023 patients with moderate to severe secondary hyperparathyroidism were randomized to receive etelcalcetide or placebo for 20 to 27 weeks, and patients in the etelcalcetide group had higher PTH levels than baseline. The proportion of patients who lost 30% was 77% and 79%, respectively, compared with 11% and 11% in the placebo group; in the etelcalcetide group, the ratio of patients with PTH ≤300 pg/mL was 52% and 56%, respectively, compared with the placebo group. The patients were only 6% and 5%.
In Japan, on December 19, 2016, Oro Pharmaceutical's Parsabiv was approved, and the drug was authorized by Amgen.
03 Emflaza (Diffkov)
On February 14, 2017, the FDA approved Emflaza (deflazacort) from Marathon Pharma, a company specializing in the development of new drugs for rare diseases, for the treatment of patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) aged 5 years and older. The approval made Embfla the first corticosteroid drug approved for the treatment of DMD worldwide and the second drug approved for the treatment of DMD worldwide. Previously, the FDA has granted Emflaza orphan drug status and priority review.
04 Siliq (brodalumab)
On February 15, 2017, the FDA approved Valeant's Siliq (brodalumab) for the treatment of adult patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are not responding to other systemic treatments. The drug is an IL-17R inhibitor that was approved by Japan PMDA on July 4, 2016. This product was originally developed by Amgen and then licensed to AstraZeneca and Kirin Pharmaceuticals of Japan. AstraZeneca gives Valeant an exclusive license to develop and sell Siliq worldwide in addition to Europe, Japan and certain Asian countries. At the same time, the two companies will share the sales profits of Siliq in the US market.
In the European Union, brodalumab was approved by the EMA on July 17, 2017 under the trade name Kyntheum and the listed holder was LEO Pharma A/S for the treatment of severe plaque psoriasis.
05 Xermelo(telotristatetiprate)
On February 28, 2017, the US FDA approved LEXICON PHARMS's Xermelo (telotristat ethyl) in combination with a somatostatin-like drug for the treatment of adult patients with carcinoid syndrome diarrhea, suitable for treating diseases with only somatostatin-like drugs. Less than controlled patients.
The safety and efficacy of Xermelo was based on a 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of 90 adult patients with well-differentiated metastatic neuroendocrine tumors and carcinoid tumor syndrome. On the basis of similar drugs using somatostatin, 33% of subjects randomized to Xermelo had a lower average number of bowel movements per day, compared with placebo-treated on the basis of somatostatin-like therapy. Only 4% of patients had a decrease in the average number of bowel movements per day.
06 Kisqali (ribociclib)
On March 13, 2017, the FDA approved Novartis' new drug Kisqali (ribociclib, formerly known as LEE011) in combination with aromatase inhibitors as an initial endocrine therapy for postmenopausal hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptors. -2 negative (HR+/HER2-) female patients with advanced or metastatic breast cancer.
Kisqali is a CDK4/6 inhibitor based on excellent phase 3 clinical trial results, which reached its primary endpoint early. The first pre-planned interim analysis showed a statistically significant improvement in Kisqali treatment with progression-free survival (PFS) compared with letrozole alone. Kisqali has received FDA-approved breakthrough therapy certification and prioritization.
On August 22, 2017, Kisqali was approved by the European Union EMA with the same indications.
Domestically, Novartis currently has eight clinical trial applications, of which three clinical trial approvals were approved as early as February 1, 2016. Six clinical trial applications were for special approval.
07 Xadago (safamide)
On March 21, 2017, the US FDA approved US WORLDMEDS's Xadago (safinamide) as an adjuvant therapy for patients with Parkinson's disease, which is currently used in levodopa/carbidopa and undergoes “off†Patients with seizures. The "off" episode is a period of time when the patient's medication does not work, which can lead to an increase in symptoms of Parkinson's disease, such as tremors and difficulty walking.
As of now, Xadago has been licensed by several European countries, including Germany, Switzerland, Spain, Italy, Belgium, Denmark, Sweden and the United Kingdom, bringing more clinical treatment options to many Parkinson patients in Europe. It is now approved by the US FDA, which brings greater market potential.
At present, many companies in China have obtained clinical trial approvals for saflufenamide mesylate tablets.
08 Symproic(naldemedine)
On March 23, 2017, the US FDA approved Symproic (Naldemedine) from Japan's Yanyeyi Pharmaceutical for the treatment of constipation caused by opioids in adult patients with chronic non-cancerous pain. Symproic is an opioid receptor blocker that specifically blocks peripheral opioid receptors and has little effect on central opioid receptors. Safety is slightly better than methylnaltrexone and naloxone. Opioid-induced constipation is a problem that every cancer patient may encounter, but there is a risk of opioid truncation symptoms, and doctors are more cautious in prescribing a prescription, which is a major reason why this kind of drug market is difficult to open, but I hope that the listing of this product will bring breakthroughs to OIC treatment.
On March 30, Yanyeyi of Yanyeyi was approved by Japan PMDA.
09 Bavencio(avelumab)
On March 23, 2017, the FDA approved Bevercio (avelumab), a PD-L1 antibody from Pfizer and Merck, Germany, for the treatment of a rare skin cancer called Merck Cellular Cancer (MCC). In a phase II clinical trial of 88 people, the objective response rate of avelumab was 33%, of which 11% were complete responses. Like other PD-1 drugs, many patients respond relatively long-lasting, with 45% of patients responding for one year.
On September 18th, avencio of Merck Serono Europe Limited was approved by the European Union EMA for the treatment of Merck cell carcinoma; on September 27, Merck Serono Co. , Ltd. The company's Bavencio Injection 200 mg was approved by Japan's PMDA and obtained orphan status in Japan.
Domestically, Merck Serono and Pfizer have three clinical trial applications, two of which have been approved, one for each. In addition, there is a phase 1 clinical trial in which the indications for solid tumors (dose escalation period), esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (dose extension phase), and a phase III clinical trial of indications for first-line treatment of non-small cell lung cancer are underway. The numbers are CTR20171035 and CTR20171000.
10 Zejula(niraparib)
On March 27, 2017, the FDA approved TESARO's Zejula (niraparib) for the treatment of recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer, maintenance of the fallopian tube or primary peritoneal cancer (to delay the growth of cancer), platinum The tumor is completely or partially contracted (completely or partially) after chemotherapy. Niraparib is a poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitor that blocks the repair of damaged DNase.
Phase 3 NOVA trials showed a 73% reduction in disease progression risk compared with placebo, with a median of 21 months for progression-free survival (PFS) and 5.5 months for placebo. From the perspective of PFS data, the efficacy of Niraparib is dramatic.
On November 16, Zejula of Tesaro UK Limited was approved by the European Union EMA.
Domestically, there is a clinical trial application with the acceptance number JXHL1700160, which was applied for by Yangsen Company and entered the sequence on September 1.
11 Dupixent(dupilumab)
On March 28, 2017, the FDA approved Sanofi (Dupilumab) for Sanofi/Regeneration, an adult patient with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis (AD) who was unable to adequately control the condition or was not suitable for these medications. . The industry is very optimistic about Dupixent's business prospects, and the company's annual sales peak is expected to exceed $2.8 billion.
Dupixent, an IL-4R alpha subunit inhibitor, is approved based on data from the global LIBERTY AD clinical program, which includes three key randomized phase 3 studies (SOLO-1, SOLO-2, CHRONOS). To evaluate the efficacy and safety of Dupixent as a single agent (SOLO-1 and SOLO-2) or in combination with topical corticosteroids (CHRONOS) for the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis (AD). The data showed that all studies achieved primary and critical secondary endpoints.
On September 27th, the EU EMA also approved Sanofi's Dupixent (dupilumab).
Domestically, Sanofi has a total of seven clinical trial applications, six of which were clinically approved on November 21, 2017.
12 Ocrevus(ocrelizumab)
On March 28, 2017, the FDA approved Roche's monoclonal antibody, Octrevus (ocrelizumab), with indications for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis and primary progressive multiple sclerosis. Ocrevus is the first and only disease-modifying treatment to simultaneously treat two types of multiple sclerosis (RMS and PPMS) and is the first and only disease-modifying treatment for PPMS. Ocrevus is a CD20 antibody that is a new target drug.
In February 2016, the FDA granted Octelus the breakthrough drug qualification (BTD) for the treatment of PPMS, becoming the first drug in the MS field to receive this honor.
Domestically, there were two clinical trial applications from Roche Pharmaceuticals. JXSL0700053 terminated the approval process on August 14, 2009; JXSL0700019 received clinical trial approval on September 30, 2009.
13 Austedo(deutetrabenazine)
On April 3, 2017, the FDA approved the launch of the Tussaud's Austedo (deutetrabenazine) for the treatment of chorea (Huntington's disease). AUSTEDO became the first FDA-approved drug.
SD-809 (AUSTEDO) is a small molecule oral inhibitor targeting VMAT-2, which is a deuterated drug for the listed Huntington's drug tetras-quinolizine. After the deuteration, the pharmacokinetic profile was improved and the half-life was significantly prolonged, allowing for lower therapeutic doses. SD-809 (AUSTEDO) was originally developed by Auspex. In March 2015, four months after the publication of Phase III clinical data of SD-809 (AUSTEDO), Teva spent $3.2 billion to acquire Auspex.
14 Ingrezza (缬benazine)
On April 11, 2017, the FDA approved Neurocrine's Ingrezza (valbenazine) for the treatment of adult tardive dyskinesia (TD). As a novel selective vesicle monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) inhibitor, INGREZZA is the first and only drug to obtain this indication. TD is a serious neurological disorder characterized by repeated involuntary movements, often involving the lower jaw, lips and tongue.
A randomized, placebo-controlled, phase III clinical trial of 6 weeks of 234 patients with moderate to severe TD showed that INGREZZA rapidly and significantly improved TD signs and symptoms, and the above improvements were clinically significant. In addition, no deterioration in subject depression, suicidal ideation, or behavior was observed in the study.
15 Brineura(cerliponase alfa)
On April 27, 2017, the FDA approved Brineura (cerliponase alfa) from BioMarin Pharma for the treatment of a super rare disease called CLN2. Brineura is the first FDA-approved treatment for late-onset infantile neuronal waxy lipofuscinosis (CLN2), also known as tripeptide peptidase-1 (TPP1) deficiency. CLN2 disease is a rare hereditary disease that usually begins between the ages of 2 and 4 years and usually includes language delays, recurrent seizures, and coordination of motor difficulties (ataxia). Affected children also develop conditions such as muscle twitching (myoclonus) and vision loss.
On May 30, Brineura was approved by the European Union EMA for the treatment of CLN2.
16 Alunbrig(brigatinib)
On April 28, 2017, FDA accelerated the approval of ARIAD's Alunbrig (brigatinib) for the treatment of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive non-small cell lung cancer, and progression or intolerance after crizotinib treatment patient. In a 222 patients with crizotinib-resistant, the overall response rates for the brigitinib 90 and 180 mg treatment groups were 48% and 53%, respectively, with complete response rates of 3.6% and 4.5%, respectively. In patients with baseline brain metastases, the intracranial ORR was 42% and 67% in the 90 and 180 mg groups, respectively.
17 Rydapt(midostaurin)
On April 28, 2017, the FDA approved Novartis's Rydapt (midostaurin, formerly known as PKC412). The first indication was the combination of chemotherapy with a newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with FLT3+ mutation. The second indication is the treatment of advanced systemic mastocytosis (SM) in adults. Rydapt is the first drug approved for the treatment of AML in 25 years. On September 18 of the same year, the EU EMA approved Rydapt.
The indication for obtaining AML this time is based on the results of the Phase III PARIFY trial. The trial screened 3279 patients with FLT3 mutations, of which 717 patients participated in the trial. Patients enrolled were treated with Rydapt in combination with cytarabine + daunorubicin. The results showed that Rydapt combination therapy significantly improved overall survival (OS) and reduced the risk of death by 23%.
Domestically, the clinical trial application for Novartis's acceptance number JXHL0800392 was approved on March 8, 2010.
18 Tymlos(abaloparatide)
On April 28, 2017, FDA approved Tymlos (abaloparatide) from RADIUS HEALTH for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis in women. Abaloparatide is a parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) analog that binds to the parathyroid receptor 1 and acts to regulate metabolism and promote bone formation. In the ACTIVE clinical trial (18 months of data) and the ACTIVExtend clinical trial (data from the first 6 months), abaloparatide reduced the risk of new vertebral fractures by 86% and the risk of non-vertebral fractures compared with placebo. 43%. In addition, the absolute risk of new vertebral fractures and non-vertebral fractures was also reduced by 3.6% and 2.0%, respectively.
19 Imfinzi(durvalumab)
On May 1, 2017, the FDA accelerated the approval of AstraZeneca's Imfinzi (durvalumab) for the treatment of metastatic bladder cancer and is the third PD-L1 inhibitor. Metastatic bladder cancer is a poorly prognostic bladder cancer with a 5-year survival rate of less than 15%. There has been no significant progress in the field for nearly 30 years. Durvalumab is a breakthrough therapy-recognized drug. ASCO's published data show that the overall objective response rate (ORR) of Durvalumab treatment is 31%, with 46% of patients with high PD-L1 expression and a disease control rate (DCR) of 48. %, PD-L1 high expression of patients was 57%.
Domestically, durvalumab has 11 clinical trial applications, and currently 9 clinical trial approvals have been approved. A phase 3 clinical trial of non-small cell lung cancer is underway, registration number CTR20170012. It can be seen that for AstraZeneca, bladder cancer is not the ultimate goal.
20 Radicava (Edala)
On May 5, 2017, the FDA first approved the marketing of Radicava (Edaravone) of MITSUBISHIE for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis treatment (ALS), which is commonly referred to as "Lu-Gregory's disease" in the United States. ALS is commonly known as gradual freezing, and the "ice bucket challenge" brought this disease into people's field of vision. A six-month clinical trial conducted in Japan confirmed that edaravone can be used for the treatment of ALS. The trial randomized 137 subjects into two groups, the edaravone experimental group and the placebo group. After 24 weeks of treatment, the daily functional assessment of the edaravone experimental group was significantly less than that of the placebo group.
On June 26, 2015, Edaravone was approved for ALS in Japan and qualified for orphan drugs. The main indication for domestic edaravone is acute ischemic stroke.
Disposable Endo Linear Cutting Stapler
An abdominal surgery disposable endo linear cutter is a surgical instrument used for cutting and stapling tissues during abdominal surgeries. It is a disposable device that is used once and then discarded. The endo linear cutter is designed to make precise cuts and staple the tissue together at the same time, reducing the risk of bleeding and improving the healing process. It is commonly used in procedures such as gastric bypass, colon resection, and other gastrointestinal surgeries. The device comes in different sizes and lengths, depending on the specific surgical procedure.
Advantage
1. Reduced risk of infection: Disposable internal cutting linear cutters are sterile and are used only once, minimizing the risk of infection.
2. Consistency: Since disposable cutters are manufactured under strict quality control measures, they offer consistent performance.
3. Convenience: Disposable cutters are easy to use and do not require any special maintenance or cleaning after use.
4. Cost-effective: Disposable cutters are often more cost-effective than reusable cutters, as they eliminate the need for expensive sterilization and maintenance procedures.
5. Improved patient safety: Disposable cutters reduce the risk of cross-contamination and infection, thus improving patient safety.
Disposable Endo Linear Cutting Stapler,Surgical Manual Disposable Stapler,Manual Linear Cutter Stapler,Disposable Endo Linear Cutter Company
Changzhou Weipu Medical Devices Co., Ltd. , https://www.cnweipumedical.com