High resolution is a reliable guarantee for confident compound detection
Key words
Accurate mass; complex matrix; gas chromatography electrostatic field orbitrap mass spectrometer; ultra high resolution; screening
Foreword
Analytical laboratories have always faced the challenge of ensuring the highest level of accuracy and improving detection efficiency on the basis of sufficient data reliability. Most of these laboratories use gas chromatography, liquid chromatography, and triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (MS) to achieve target compound detection. The above analytical techniques can detect a wide range of compounds with widely varying properties within a range of sensitivity levels and selectivity requirements, but the limitations are in the list of target compounds that need to be determined and require targeted mass spectrometry parameters for each compound. Optimization. Using the electrostatic field orbitrap (Orbitrap) technology to analyze the sample and obtain high-resolution full-scan data can easily solve the following challenges:
• Simultaneous qualitative and quantitative analysis of rapidly growing compounds • Purposeful retrospective analysis of data collected in the past • Requirements for qualitative identification analysis of chemical elemental composition and structurally unknown compounds
So far, the success of electrostatic field orbital technology combined with liquid chromatography has fully proved its important value as an efficient analytical method. 1 The newly released Thermo Scientific TM Q Exactive TM GC hybrid quadrupole-Obitrap MS system now enables the combination of Orbitrap technology and gas chromatography. This new benchtop quadrupole-orbitrap mass spectrometer opens up a new era of analysis for compounds suitable for gas chromatography. The following analysis examples will highlight the powerful analytical advantages of gas chromatography coupled with high resolution mass spectrometry.

The importance of mass resolution for detection selectivity of target compounds
High-resolution accurate mass (HR/AM) detection performs mass-scan analysis of samples. For small-molecule compound analysis, the scan range is generally set to 50-1000 Da. The high resolution capabilities of Orbitrap technology effectively distinguish target compounds from other compounds with similar mass numbers as well as matrix interferences. In the detection of the target compound, the target ion is subjected to extraction analysis (usually < 5 ppm) within a narrow mass window. High-resolution mass spectrometers provide high-quality, accurate data while maintaining high-quality resolution, and only when both are available to achieve accurate extraction of target compound ions in such a narrow mass window. When the resolution is not high enough, the mass spectral peaks of the two compound ions may overlap, and the measured mass spectrum peak is the combination of the mass numbers of the two compound ions. The overlap of such mass numbers can directly lead to large deviations in the mass number detection results of the target compound. Such problems are shown in Figure 1. The amaranth extract extracted by the QuEChERS method was dissolved in acetone solution and the resolution was tested four times at 15K, 30K, 60K and 120K (m/z 200) mass resolution.
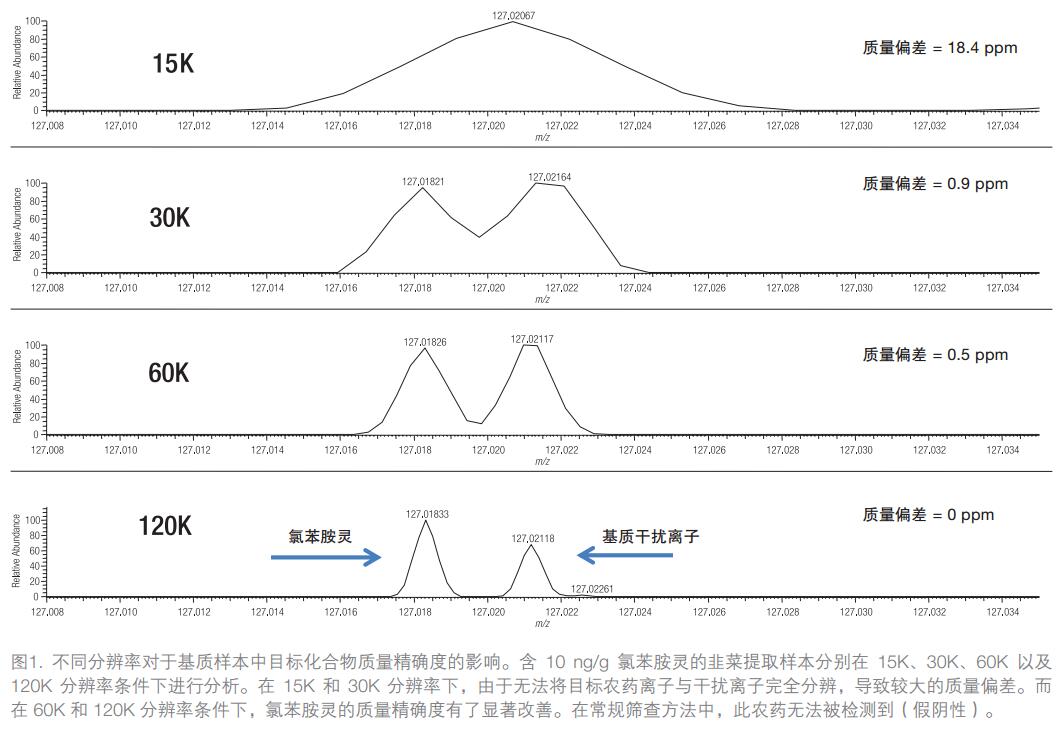
The above mass spectrum shows that the pesticide chlorpheniramine (m/z 127.01833) interferes with a background ion with a similar mass-to-charge ratio in the matrix. At 60K and 120K resolution, the chloroaniline and interfering ion mass spectral peaks are essentially baseline separated, resulting in an accurate mass with minimal deviation. However, under the conditions of 15K and 30K resolution, the measured mass and the theoretical value deviate greatly due to the inability to effectively distinguish the chloroaniline and the interfering ions. At 15K resolution, the mass deviation reaches 18.4 ppm. Usually, in the screening experiment, the mass error range is set to < 5 ppm, and the maximum range can be increased to 10 ppm, and the above quality deviation can cause the pesticide screening result to be false negative (not detected). This example clearly demonstrates that screening experiments have minimum requirements for setting mass resolution. The limit value of the lowest mass resolution depends on the complexity of the sample to be tested and the concentration of the target compound and interfering substance.
Good sensitivity at high resolution
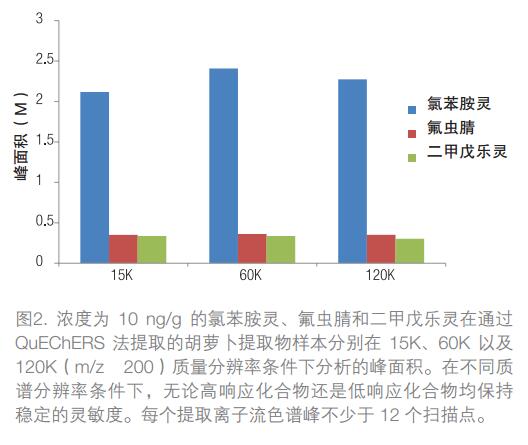
Other types of gas phase-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) combined techniques can result in a decrease in ion transport efficiency while increasing mass spectral resolution. This has an impact on the sensitivity and accuracy of the detection. For low-level target compound screening and quantitative analysis in complex matrices, sufficient sensitivity must be ensured while achieving high-quality resolution. In Figure 1, the need for high resolution is clearly demonstrated. Then, under the premise that mass resolution is very important, it is especially necessary to ensure sensitivity at 60K and 120K high resolution. Unlike other types of mass spectrometers, the Q Exactive GC system provides a significant reduction in signal sensitivity without increasing mass resolution. Figure 2 shows the peaks analyzed in the 15K, 60K, and 120K resolution modes for three pesticides (chloranilide, fipronil, and pendimethalin) at 10 ng/g in the carrot extract sample extracted by the QuEChERS method. area. The above sample analysis of the extracts uses the first-level full scan mode for data acquisition in all three resolution modes. Its stable performance allows the instrument to obtain accurate masses with extremely high accuracy by improving mass resolution without sacrificing sensitivity.
Identification of unknown compounds using high resolution mass spectrometry
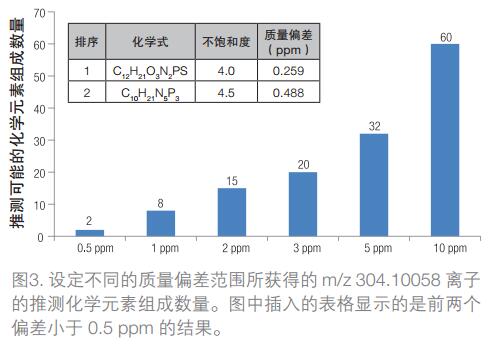
Obtaining accurate mass numbers in full scan mode is one of the advantages of Orbitrap technology, which allows for retrospective analysis of past data to identify and identify unknown peaks. Under the condition that the accurate mass number is accurate, the elemental composition of the unknown compound can be estimated by the measured accurate mass and the isotope ratio. The number of possible results for the speculative chemical element composition depends on the type of chemical element selected in the calculation module and the quality of the mass spectrometry data. In high resolution mode, analytical data that guarantees a mass deviation of less than 1 ppm can control the possible chemical elemental composition of the target unknown compound to a minimum. The speculative result of the element composition is shown in Fig. 3. The number of possible elemental composition results of an ion measured as m/z 304.10058 is calculated by the element composition calculation module, wherein the number of each chemical element ranges from: carbon (C) 1–50, hydrogen ( H) 1–50, oxygen (O) 1–20, nitrogen (N) 1–20, phosphorus (P) 1–10, sulfur (S) 1–10.
The mass deviation range varies from 0.5 to 10 ppm, and the estimated number of possible chemical formulas is shown in Figure 3. As expected, the wider the range of mass deviations, the more speculative chemical formulas are speculated. With a set deviation of 10 ppm, 60 possible elemental compositions were inferred. Even if the mass deviation range is reduced to a relatively low 3 ppm, 20 possible elemental compositions are listed. However, when the mass deviation is reduced to less than the 1 ppm range normally allowed by the Q Exactive GC system, the speculative result is left with only two chemical elements with a deviation of less than 0.5 ppm. Among them, the first speculated result was C12H21N2O3PS with a deviation of 0.3 ppm. The results were submitted to the ChemSpider online database for retrieval, and the results were ranked first in the pesticide diazinon. Subsequent structural identification can be matched by analyzing the fragment ions obtained by electron bombardment (EI) with a standard library.
in conclusion
• The Thermo Scientific Q Exactive GC mass spectrometer with unparalleled conventional high-quality resolution and stable sub-ppm mass accuracy is a unique and powerful tool for compound detection, screening, quantification, and identification and structural resolution of unknown compounds.
• Effectively distinguishes chloroaniline from background interfering ions, requiring a mass spectrometer resolution of not less than 60,000 FWHM (m/z 200). This resolution requirement is also necessary for the detection of other compounds.
• The Q Exactive GC mass spectrometry system provides highly sensitive analytical results for target compound detection in complex matrix samples and, more importantly, at different mass spectral resolutions (at m/z 200, standard mass resolution of 15–120 KFWHM) The instrument always maintains high sensitivity.
• Superior sub-ppm quality accuracy accelerates the identification process of unknowns by reducing the range of mass deviations.
references
1.Thermo Scientific Application Note 617: Quantitative and Qualitative Confirmation of Pesticides in Beet Extract Using a Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer. San Jose, California, USA and Bremen, Germany. [Online] http:// Content/dam/tfs/ATG/CMD/cmd-documents/sci-res/app/ms/lc-ms/Orbitraps/AN-617-LC-MSMS-PesticidesBeets-AN64284-EN.pdf (accessed May 1, 2015) .
Air Hose Reel,Mini Air Hose Reel,Air Compressor Hose Reel,Industrial Air Hose Reel
NINGBO QIKAI ENVIRONMENTAL TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.hosereelqikai.com