Summary of research progress in the field of cardiovascular disease (02.01)
Summary of research progress in the field of cardiovascular disease (02.01)
February 01, 2018 Source: WuXi PharmaTech
Window._bd_share_config={ "common":{ "bdSnsKey":{ },"bdText":"","bdMini":"2","bdMiniList":false,"bdPic":"","bdStyle":" 0","bdSize":"16"},"share":{ }};with(document)0[(getElementsByTagName('head')[0]||body).appendChild(createElement('script')) .src='http://bdimg.share.baidu.com/static/api/js/share.js?v=89860593.js?cdnversion='+~(-new Date()/36e5)];1. FDA approved chronic myocardial ischemia therapy trial
BioCardia has announced that the US FDA has approved the Clinical Trial Equipment Exemption (IDE) for the CardiAMP Chronic Myocardial Ischemia (CMI) trial to treat patients with refractory angina (RA).

An estimated 600 to 1.8 million people in the United States have RA, with approximately 75,000 new cases each year. Although revascularization techniques have improved over the years, there are still more and more patients with chronic refractory angina who cannot accept more revascularization because of severe symptoms. The physiological and mental health of these patients is worrying, the quality of life is significantly impaired, and the pressure on the medical system can be caused. Therefore, there is still a large medical need that is not met in this type of patient.
CardiAMP Cellular Therapy is an individualized minimally invasive therapy that uses the patient's own cells to treat cardiovascular disease. The therapy is designed to stimulate the body's natural healing response. The CardiAMP CMI trial will be a prospective, multicenter, randomized, sham-controlled, double-blind, key trial to validate the safety and efficacy of CardiAMP in the study of cell therapy in patients with CMI with RA. The trial has been approved for registration of 343 subjects in 40 US centers.
“The FDA's approval of the CardiAMP CMI trial is another important milestone for the company,†said Dr. Peter Altman, CEO of BioCardia. “This is another step toward a new treatment strategy that could have a huge benefit for patients with refractory angina. The approval of the second key trial further demonstrates BioCardia's leadership in the treatment of heart disease."
2. Mesp1 gene plays an important role in heart development
Recently, researchers at the Université libre de Bruxelles and the University of Cambridge identified the role of the gene Mesp1 in the earliest stages of cardiovascular lineage segregation, a finding that helps to understand the congenital heart. defect. Related papers were published in Science.
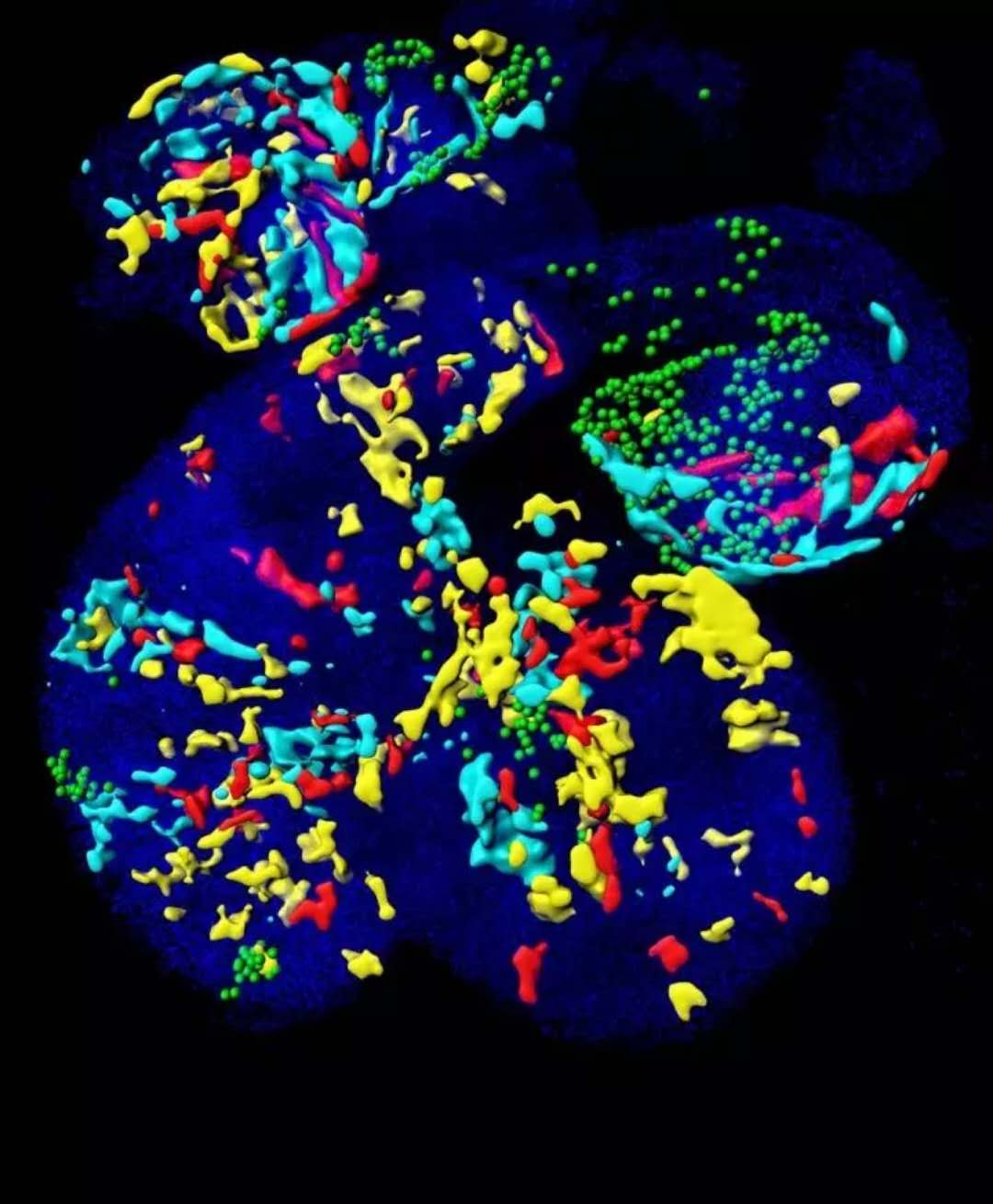
â–² This is a mosaic-marked embryonic heart. Each color patch is derived from an early marker of cardiac progenitor cells expressing the key gene Mesp1. (Source: EurekAlert)
The heart is the first organ that develops during development and consists of four regions (the ventricles and the atria) that contain different cells that perform different functions. The heart progenitor cells need to be produced at the right time, migrate to the right place, and differentiate into the correct cell type, otherwise severe heart malformations will occur. In human patients, this cardiac malformation is considered congenital heart disease, which is the most common cause of severe birth defects in infants. Previous studies have shown that multiple cardiac progenitor cells are derived from different cell populations that express the Mesp1 gene. However, how to distinguish various progenitor cells at the molecular level, and which molecular mechanisms promote specific cardiac regions or cardiac lineages, remains to be elucidated. In the paper, the researchers determined the role of Mesp1 in the earliest stages of cardiovascular lineage separation by single cell molecular profiling and lineage tracking.
The researchers isolated Mesp1-expressing cells at different stages of embryonic development and performed single-cell transcriptome analysis on these early cardiac progenitors, demonstrating that different cardiac progenitor cell populations have different molecular characteristics. The researchers also performed single-cell molecular analysis of these early progenitor cells in the absence of Mesp1. Experiments have shown that Mesp1 is required for cells to exit from pluripotent states and induce cardiovascular gene expression. In these early progenitor cells expressing Mesp1, the researchers identified molecular features associated with early lineage restriction and cardiac region segregation. The researchers also identified the earliest branch points between the cardiac cell lineage and the vascular cell lineage.

▲ Professor Cédric Blanpain of Cambridge University (Source: Cambridge University)
"Future research will need to determine whether the patterns of early cell lineage segregation found here control the formation of different cell lineages in different organs and tissues, and whether the molecular features revealed here play a role in congenital heart malformations, and Whether it is used to push cardiovascular progenitor cells into a specific lineage may be important for advancing cell therapy for cardiac repair," said one of the senior authors of the paper, Professor Cédric Blanpain of the University of Cambridge.
3. The latest research data of acute ischemic stroke arterial thrombectomy
Penumbra recently announced the results of the company's funded acute ischemic stroke arterial thrombectomy PROMISE study at the International Stroke Conference (ISC 2018) in Los Angeles. The study used A direct aspiration first pass technique (ADAPT) to treat acute ischemic stroke, demonstrating the safety of the Penumbra thrombectomy system using ACETM68 and ACETM64 reperfusion catheters as first-line therapy. And effectiveness.

At present, the number of deaths due to stroke in China has exceeded that of cancer and cardiovascular disease, making it the first cause of death. Acute ischemic stroke is the infarction of brain tissue caused by occlusion of cerebral arteries. It is the most common type of stroke, accounting for 60% to 80% of all stroke cases in China. Cerebral ischemia leads to rapid death of cells in the ischemic core region, but studies have found that within a few hours after cerebral ischemia, a region between the core region and healthy brain tissue, such as timely treatment, may be saved. This area is called "Ischemic penumbra" (Penumbra).
The Penumbra System® is a fully integrated system designed specifically for mechanical thrombectomy and was first approved by the US FDA in December 2007 for a 510(k) license. The system acts on the proximal surface of the thrombus and gently draws the thrombus from the intracranial blood vessels through a suction platform for revascularization in patients with acute ischemic stroke of intracranial large vessel occlusion.
The PROMISE study is a prospective, one-arm, multicenter study designed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the Penumbra thrombectomy system using ACETM68 and ACETM64 reperfusion catheters. The study enrolled a total of 204 patients in 20 centers in Europe. The primary endpoints included the revascularization rate (2b-3 points) of the mTICI score assessed by the independent core laboratory, and the clinical independence (0-2 points) measured by the modified Rankin score (mRS) at 90 days. The results showed that the revascularization rate reached 93.1%, and 39.2% of the patients achieved mTICI 3 grade revascularization. Clinical independence at 90 days reached 61%. Key secondary safety-related endpoints also showed excellent results: all-cause mortality was 7.5% at 90 days, symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH) was 2.9% at 24 hours, and 1.5% of new-onset (ENT) embolization. The median time to surgery, and the time from inguinal puncture to mTICI grade 2b-3 revascularization, was 31 minutes (20.0-53.0 minutes).

â–² Dr. Adam Elsesser, Chairman, CEO and President of Penumbra (Source: Penumbra)
Dr. Adam Elsesser, Chairman, CEO and President of Penumbra, said: "We are grateful to all PROMISE researchers for providing global evidence for ADAPT as a first-line therapy for patients with acute ischemic stroke. The PROMISE study reinforces our belief that ACE68 The Penumbra system provides a fast, safe and cost-effective method for revascularization of ischemic stroke."
Reference materials:
[1] CardiAMP Cell Therapy Receives FDA Approval for Pivotal Trial in Chronic Myocardial Ischemia
[2] From stem cells to a functional heart: The role of the Mesp1 gene
[3] Penumbra Shows Off Real-World Study Data in Acute Ischemic Stroke Trial
Original Title: Summary of Research Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases (No. 24)
Ventilation is one of the most important components in a successful greenhouse.
If there is no proper ventilation, greenhouses and their growing plants can become prone to problems. The main purposes of ventilation are to regulate the temperature and humidity to the optimal level, and to ensure movement of air and thus prevent build-up of plant pathogens (such as Botrytis cinerea) that prefer still air conditions. Ventilation also ensures a supply of fresh air for photosynthesis and plant respiration, and may enable important pollinators to access the greenhouse crop.
Circulation Fan,Greenhouse Ventilation Fan,Automated Greenhouse Ventilation Fan
JIANGSU SKYPLAN GREENHOUSE TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.engreenhouse.com