Ultrasound is helpful in diagnosing median nerve palmar injury
Release date: 2016-09-22
 The median nerve palmar branch (PCBMN) is separated from the median nerve before the distal median nerve (MN) of the forearm enters the carpal tunnel. PCBMN passes through the surface of the wrist flexor support band and issues a branch-dominant wrist and large fish. The feeling of being everywhere. At the distal end of the carpal tunnel, the median nerve has three branches that respectively dictate the feeling of three and a half fingers on the lateral side of the palmar striate (Fig. 1A). PCBMN injury is common after carpal tunnel syndrome. In addition to this iatrogenic injury, PCBMN damage is quite rare.
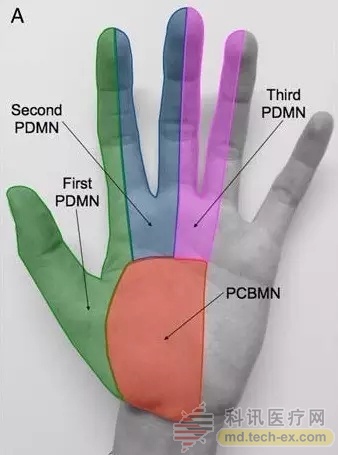
Figure 1A PCBMN and MN carpal distal three branches of the sensory dominating area
Zanette et al. from the Pederzoli Hospital in Italy reported a case of PCBMN injury in the July 2016 issue of American journal of physical medicine & rehabilitation. The patient, male, 60 years old, with a loss of palmar sensation/abnormal pain after a glass cut in the left wrist. The abnormal area is shown in Figure 1B, and the left wrist is Tinel sign (+).

Figure 1B Patient's paresthesia area
Nerve conduction (NCS) examination showed that the left PCBMN was deficient in sensory nerve action potential (SNAP) and the sensory nerve potential of the remaining nerve branches was normal (Fig. 1C). The results of the muscle needle electromyography of the left muscle composite muscle action potential and the left hand interneuronal nerve were normal.
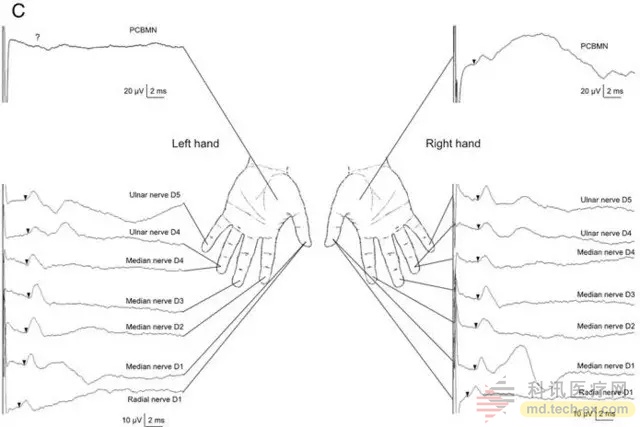
Figure 1C left forward PCBMN sensory nerve action potential (the SNAP) deletion, sensory nerve potential test I branch of median nerve were normal.
Ultrasound was performed because the sensory damage was beyond the distribution of the palmar cortex. Neurosurgery showed an increase in the cross-sectional area of ​​the left PCBMN, suggesting a local neuroma (Fig. 2A). In addition, at the distal end of the PCBMN nerve trunk, the bundled lesion of MN is visible in the wrist (Fig. 2B). The second physical examination also showed a Tinel sign in the above two parts. Surgical exploration confirmed bundled MN lesions at the distal end of the carpal tunnel.
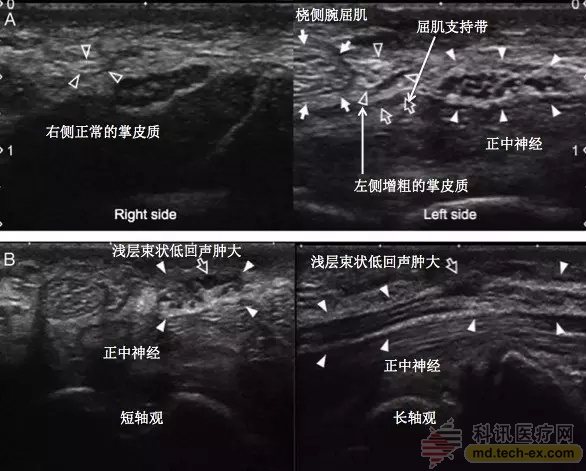
Figure 2A Ultrasound examination of the median nerve and palmar cortex on the left and right side; Figure 2B Ultrasound examination of the short-axis and long-axis section of the median nerve on the left side
The above case is a case of a neuroma with atypical PCBMN injury on the left side. Two points can be drawn: one is the application value of neurosurgery in the peripheral nerve, and the other is to pay attention to the distribution characteristics of the median nerve sensory fiber bundle.
The patient's nerve conduction velocity test suggested PCBMN injury, but a comprehensive examination revealed that the sensory abnormality area was beyond the scope of PCBMN dominance (Fig. 1B), so further evaluation was performed using neuro-ultrasound to find possible multiple lesion sites. The case also evaluated the PCBMN and the distal MN portion of the carpal tunnel. The PCBMN was the primary cutting injury, and the distal MN portion of the carpal tunnel may have secondary damage to the trauma. "Double crush" may be the pathogenesis of this case, that is, the secondary nerve secondary changes after the proximal nerve is compressed. The MN lesion at the distal end of the carpal tunnel was found during surgery, confirming this hypothesis. At the same time, the two Tinel signs appearing in the second physical examination also support this speculation. Neurosonography excluded the anatomical variation of PCBMN and found two lesions, PCBMN and distal MN of the carpal tunnel.
This case report suggests that electrophysiological examination and neuro-ultrasound complement each other can improve the accuracy of diagnosis of peripheral nerve damage.
Source: Lilac Garden
China Extract Powder For Use As Dietary Supplement Extract Powder, Extract Powder Manufacturer
Shaanxi Kang New Pharmaceutical co., Ltd. , https://www.bodybuildingoil.com