Science: A new way to produce 3D nano DNA particles
Release date: 2016-06-02
An article published online by Science on May 26 reported that scientists have developed a new way to routinely construct 3D nanoparticles using DNA strands, which can be used in vaccines, genetic modification tools, and memory storage.
Self-designed DNA origami new method
Researchers can use DNA strands to construct nanostructures in almost every form and type. However, these particles are designed by hand through a very laborious process. This restrictive method is called DNA origami, which is limited by the need for a forward design of a specific Watson-Crick base pairing for any given target structure, so only a few experts have studied under this topic. .
Since the traditional DNA origami is not like, the main construction process is by hand. MIT professor Mark Bathe led a study that began with a simple three-dimensional geometric representation of the final shape of the particles to determine how to assemble the DNA.
This is a versatile, top-down strategy that can design almost any DNA architecture based on the target form. The object appears as a closed surface to present a polyhedral network of parallel DNA double strands, which allows the complete DNA scaffold structure to be arranged in a tree-generated algorithm.
Asymmetric polymerase chain reaction can be applied to the production of stable, monodisperse components. The length of the scaffold and sequence was custom and its high fidelity was verified on a 3D using a single particle cryo-electron microscope. The long-term stability of these DNA nanoparticles in serum and in low salt buffers demonstrates the effectiveness of their biological effects as well as non-biological uses.
Can be used to develop different nanoparticles
This method can also be used to develop different nanoparticles for a wider range of applications, including scaffolds for vaccines, vectors for genetic modification tools, and memory storage files.
Bathe mentioned: "We hope that the automation of this approach will expand the participation of other non-professional researchers in the use of this highly effective molecular design paradigm."
This method represents the very simple and stable definition of its substrate. Then it breaks the sequence of the substrate into the polygon. It then uses an extended single-stranded DNA as a scaffold to assemble through all of the building blocks.
This method organizes the scaffold in a fast and environmentally friendly step that can be applied to any form of 3D object. Bathe said: "This step is part of this powerful approach. It does not require any guidance or human-machine interface. It guarantees that any three-dimensional object will work very efficiently."
This method is named DAEDALUS (DNA Origami Sequence Design Algorithm for Consumer, a DNA origami sequence design method for customers). It is constructed like a maze constructed by Greek artisans and artists. It can also be used to construct any type of three-dimensional structure. .
Source: Bio-Exploration
Color waxy corn is generally white, yellow, red, purple and black, white, yellow and purple corn is the basic color. The purple gene in a purple/white hybrid will naturally become purple if it "beats" the white gene, and vice versa, if it's a tie, what we see is a white/purple corn. Purple can turn into red corn and black corn, which is often called "red is purple, black is purple."
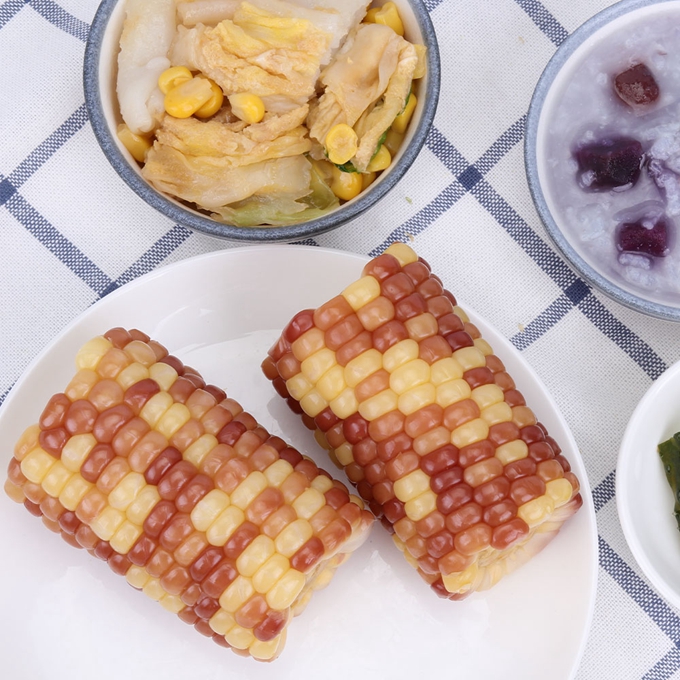
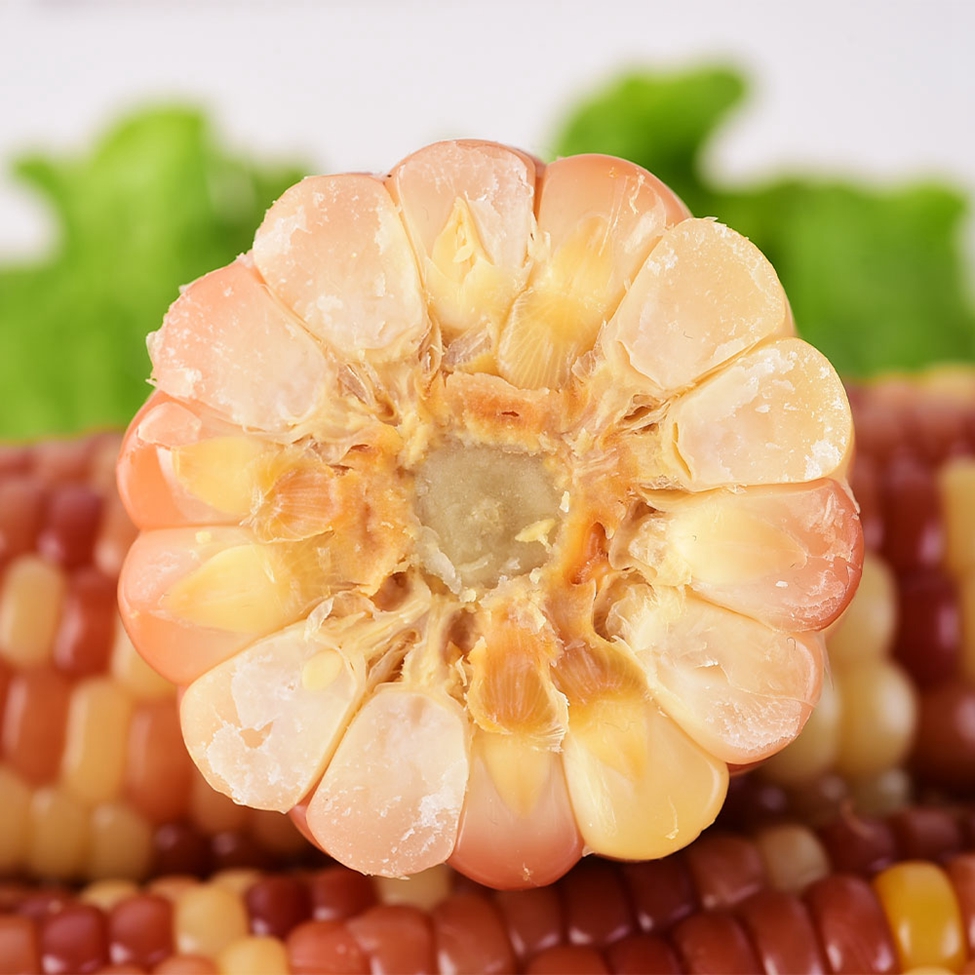
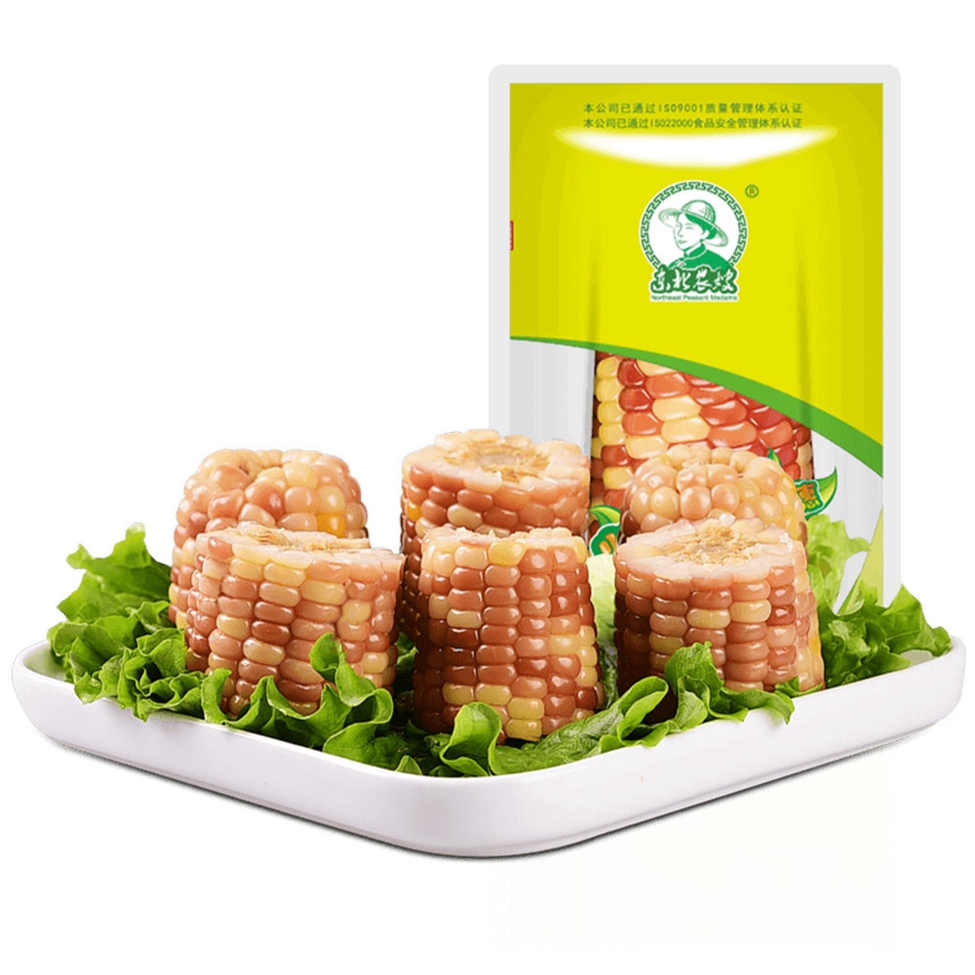



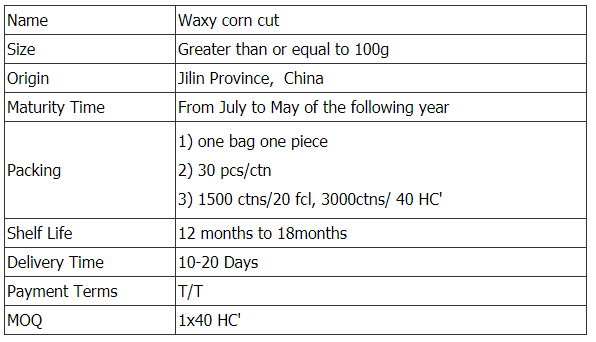
Mottled Corn Cut,Non Gmo Corn Cob,Mottled Waxy Corn Cut,Non Gmo Corn Cob Cut
Jilin Province Argricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. , https://www.nongsaocorns.com