Electronic skin can be compared to real skin while feeling the pressure of a hair
Release date: 2015-11-03
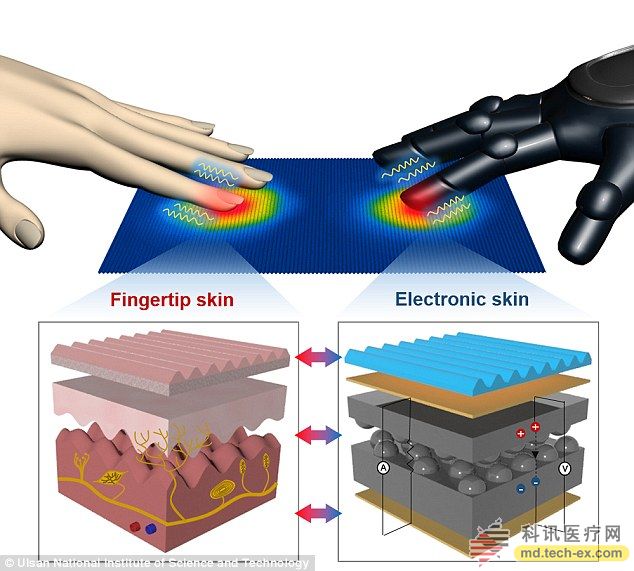
A few days ago, the ability of finger skin to feel temperature and pressure has been replicated by electronic “skinâ€.
In the test, the electronic skin glove was able to detect water droplets across the fingertips of the glove while even detecting the hair placed on its surface. This breakthrough will be used for many bionic prostheses and will improve the accuracy of wearable sensors and medical diagnostic equipment.
Professor Jonghwa Park of the Ulsan National Institute led the development of electronic skin.
Human skin includes unique epithelial and dermal microstructural and sensory receptors. The micro-ridge structure at the fingertip is designed for fine-tuning of epidermal sensing while transmitting sensory information to the brain.
Today's electronic skin technology allows robots and machine prostheses to grasp and manipulate objects, to distinguish the texture and hardness of the surface of the object, while also sensing the temperature of the object. However, the simultaneous detection of temperature and different types of high-sensitivity pressure by electronic skin is still a problem.
Professor Park and his colleagues designed iron-plated films to mimic the “mountain†structure of human fingertip skin. By increasing the polymer composition and reducing the graphene content, the film is able to detect the touch and temperature using the perceived charge.
Researchers use water droplets to detect the response of electronic skin to sensory changes, and the results show that electronic skin can sense different pressures and temperatures of water droplets. At the same time, the electronic skin can also sense the tiny pressure generated by the hair.
Professor Park and his team said that when exposed to human wrists, electronic skin can sense changes in body temperature caused by vasodilation and contraction.
Last month, Stanford University developed a tactile artificial skin that not only senses stress but also transmits signals to nerve cells. They hope that the concept test will be further transformed into the development of artificial hands that can sense different textures and distinguish between hot and cold.
Original link: http://
Source: Kexun Medical Network
8 Inch Face Access Control,8-Inch Touch Screen Access Control Device,8 Inch Face Recognition Attendance Access Control,Face Recognition Attendance Access System
Shenzhen BIO Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.huifantech.com