PH introduction of pure water and ultrapure water
Pure water / ultrapure water PH
For a long time, customers often question the PH of pure water. There are usually two types of problems . One is that RO water is weakly acidic ( around 6.0 ), and the other is RODI water (even reaching a resistivity of 10M or more). Also acidic ( PH = 6.0 or so). Â Â
First of all, it is normal for the RO water to be weakly acidic . The primary pure water obtained by the RO technology is basically weakly acidic, which is caused by the fact that the dissolved CO2 in the tap water cannot be removed. The principle is as follows: Â
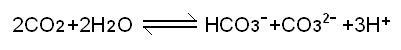
CO2 is dissolved in water, and the above chemical equilibrium exists. Since CO2 is equivalent to water molecules, RO membrane cannot be removed.
Gaseous CO2 , but HCO3- and CO3-- can be removed by most, and the large reduction of the product will cause the chemical reaction to move to the right, and the H+ concentration of the other product will increase, resulting in a decrease in the pH of the RO produced water. Weakly acidic. Â
Therefore, RO water in a certain range of applications will receive limited, but it is still in line with national standards laboratory water requirement of three, in the CLASS III standard, allowing pure water PH between 5.0 and 7.5, so all requirements The application of tertiary water, RO water is an ideal choice, RO method is also recognized as a purification method. Restricted applications include areas where PH is strictly required , such as industrial cooling water. The weakly acidic RO water has the risk of causing corrosion of metal pipes. Therefore, we usually use demineralized water as cooling water, the cost is low, and PH is guaranteed. Very high equipment, there are also requirements to use more than 10M of water as cooling water, which of course does not have to consider the PH problem (it must be neutral). Â
For high-purity water with a water quality above 10M , the measured pH is acidic. The conclusion is wrong, which is completely different from the acidity measurement of RO water. This result is a typical method error. Â Â
The pH measurement of high-purity water requires special means and instruments. The general pH meter is designed to test electrolyte solutions with high salt content, and is not suitable for measuring ultra-pure water with extremely poor conductivity and extremely unsaturated. Easy to absorb external impurities). If the resistivity meter is reliable, of course, there is no need to do this unnecessary PH measurement. Â National standard (GB6682-92) As pointed out in the laboratory water, as a pair, two measurements do not advocate the pH of water, ultra-pure water is measured accurately even harder.
Attached: China National Standards Analytical Laboratory Water Specifications and Experimental Methods GB/T6682-2008
Name | First level | Second level | Third level |
  p H range ( 25 ° C ) | - | - | 5.0-7.5 |
Specific resistance ( MΩ.cm.25 °C ) ≥ | 10 | 1 | 0.2 |
Oxidizable substances [ in ( 0 ) ] , mg/L | - | 0.08 | 0.4 |
Absorbance ( 254nm, 1cm pathlength) ≤ | 0.001 | 0.01 | - |
Evaporation residue ( 105±2 °C ), mg/L≤ | - | 1 | 2 |
Soluble silicon [ as ( S iO 2 ) ] , mg/L< | 0.01 | 0.02 | - |
China Extract Powder For Use As Dietary Supplement Extract Powder, Extract Powder Manufacturer
Shaanxi Kang New Pharmaceutical co., Ltd. , https://www.bio-pharmacies.com